Version: This documentation is based on Keycloak 26.5.2
Source: keycloak/keycloak
This document explains the “Full Scope Allowed” setting in Keycloak, how it affects token content, security implications, and best practices for production environments.
What is Full Scope Allowed?
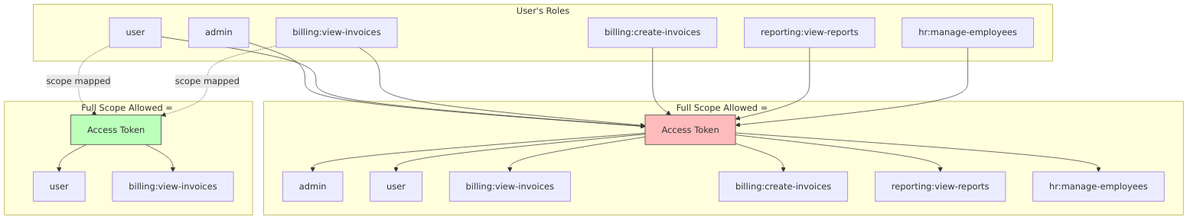
Full Scope Allowed is a client-level setting that controls which roles appear in access tokens. When enabled, all roles assigned to a user are included in tokens issued for that client. When disabled, only roles that are explicitly mapped through scope mappings are included.
The Security Problem
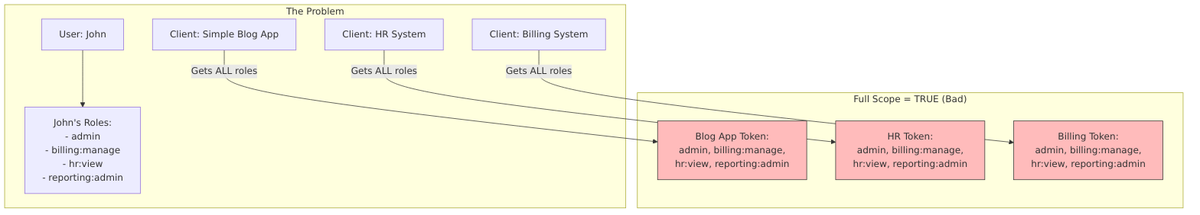
By default, when Full Scope Allowed is enabled:
- Over-privileged tokens: Applications receive more permissions than they need
- Principle of Least Privilege violation: Users’ full role set is exposed to every client
- Attack surface expansion: Compromised tokens grant access to all user roles
- Cross-application data leakage: Client A sees roles meant for Client B
How It Works (Source Code)
ClientModel Interface
From ClientModel.java:197-198:
boolean isFullScopeAllowed(); void setFullScopeAllowed(boolean value);
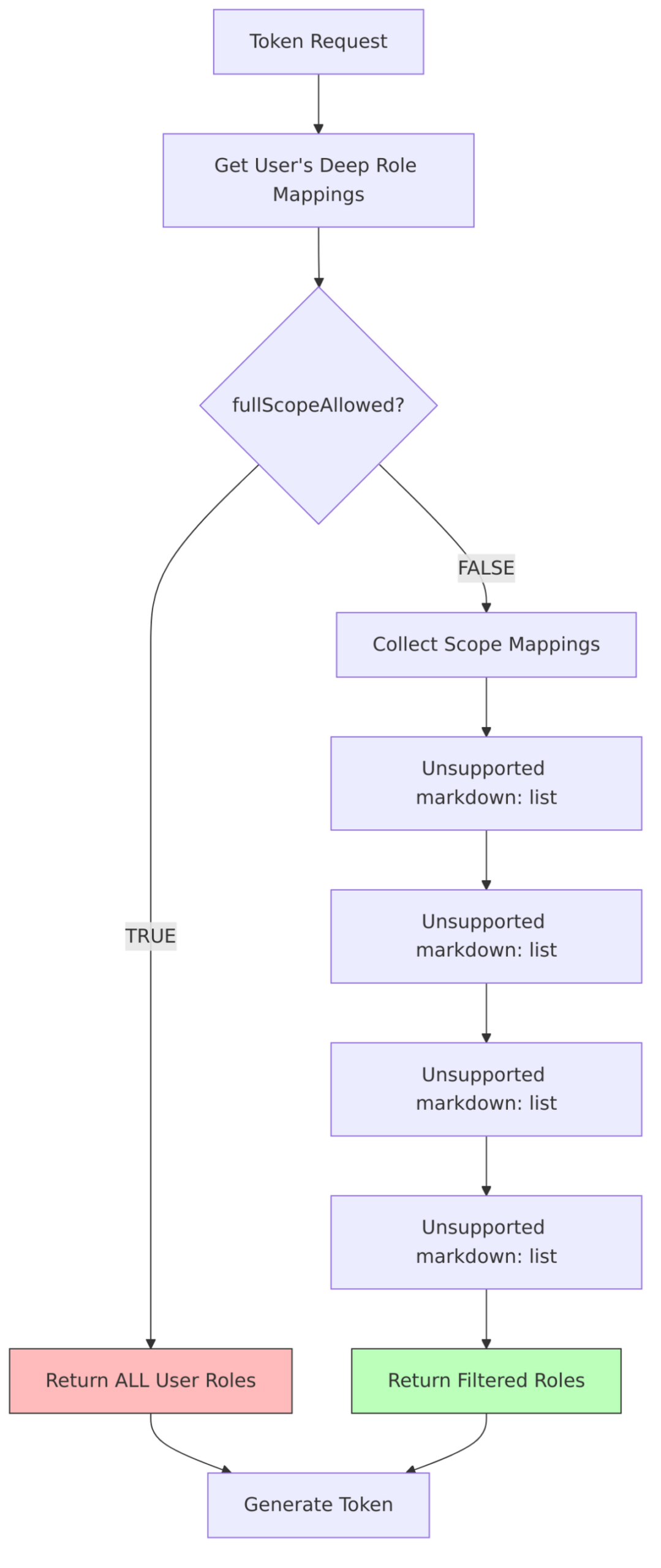
Token Generation Logic
From TokenManager.java:602-636:
public static Set<rolemodel> getAccess(UserModel user, ClientModel client,
Stream<clientscopemodel> clientScopes) {
// Get ALL roles the user has (deep resolution including composite roles)
Set<rolemodel> roleMappings = RoleUtils.getDeepUserRoleMappings(user);
if (client.isFullScopeAllowed()) {
// Return ALL user roles - no filtering
logger.tracef("Using full scope for client %s", client.getClientId());
return roleMappings;
} else {
// 1. Start with client's own roles
Stream<rolemodel> scopeMappings = client.getRolesStream();
// 2. Add role mappings from all client scopes
Stream<rolemodel> clientScopesMappings = clientScopes
.flatMap(clientScope -> clientScope.getScopeMappingsStream());
scopeMappings = Stream.concat(scopeMappings, clientScopesMappings);
// 3. Expand composite roles
scopeMappings = RoleUtils.expandCompositeRolesStream(scopeMappings);
// 4. INTERSECTION: Keep only roles that user has AND are in scope
roleMappings.retainAll(scopeMappings.collect(Collectors.toSet()));
return roleMappings; // Filtered roles
}
}
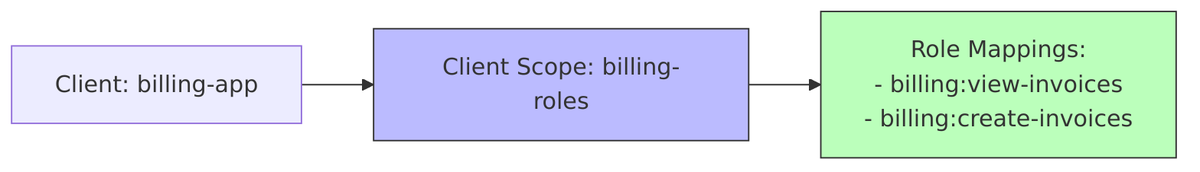
Role Resolution Flow
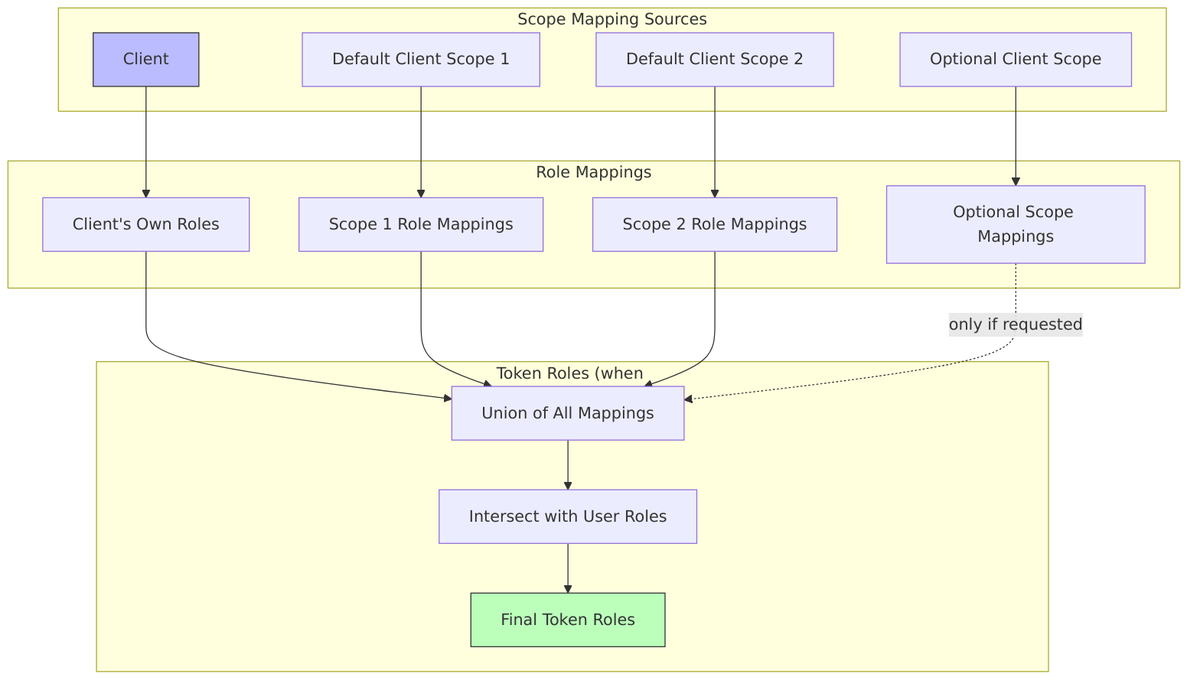
Scope Mappings Explained
When Full Scope Allowed is disabled, roles in tokens are determined by scope mappings.
ScopeContainerModel Interface
From ScopeContainerModel.java:
public interface ScopeContainerModel {
// Get all roles mapped to this scope
Stream<rolemodel> getScopeMappingsStream();
// Get only realm-level role mappings
Stream<rolemodel> getRealmScopeMappingsStream();
// Add a role to scope mappings
void addScopeMapping(RoleModel role);
// Remove a role from scope mappings
void deleteScopeMapping(RoleModel role);
// Check if role is in scope
boolean hasScope(RoleModel role);
}
Where Scope Mappings Come From
Scope Mapping Resolution
From DefaultClientSessionContext.java:303-307:
private Set<rolemodel> loadRoles() {
UserModel user = clientSession.getUserSession().getUser();
ClientModel client = clientSession.getClient();
// This calls TokenManager.getAccess() which applies fullScopeAllowed filtering
return TokenManager.getAccess(user, client, getClientScopesStream());
}
Default Values by Client Type
From Keycloak’s realm initialization code:
| Client Type | Default fullScopeAllowed | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Admin Console | true |
Needs all admin roles |
| Admin CLI | true |
Needs all admin roles |
| Realm Management | false |
Bearer-only, restricted access |
| Account Management | false |
Limited to account operations |
| Account Console | false |
Limited to account operations |
| Broker Service | false |
Limited to broker operations |
| User-created clients | false |
Security best practice |
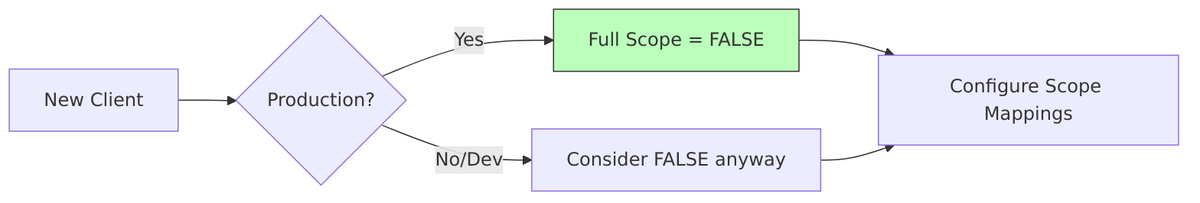
Important: New clients created through Admin Console or API have fullScopeAllowed = false by default.
Token Comparison
With Full Scope Allowed = TRUE
{
"sub": "user-123",
"realm_access": {
"roles": [
"admin",
"user",
"offline_access",
"uma_authorization"
]
},
"resource_access": {
"billing-service": {
"roles": ["view-invoices", "create-invoices", "delete-invoices"]
},
"hr-system": {
"roles": ["view-employees", "manage-employees"]
},
"reporting-service": {
"roles": ["view-reports", "export-reports", "admin"]
},
"account": {
"roles": ["manage-account", "view-profile"]
}
}
}
With Full Scope Allowed = FALSE (Properly Configured)
{
"sub": "user-123",
"realm_access": {
"roles": [
"user"
]
},
"resource_access": {
"billing-service": {
"roles": ["view-invoices"]
}
}
}
Configuration Guide
Step 1: Disable Full Scope Allowed
In Admin Console: Clients ? Select client ? Settings ? Full scope allowed = OFF
Or via API:
curl -X PUT \
"https://keycloak.example.com/admin/realms/myrealm/clients/{client-id}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"fullScopeAllowed": false}'
Step 2: Configure Scope Mappings
Option A: Client Scope Role Mappings
- Clients ? Select client ? Client scopes tab
- Select a default or optional client scope
- Scope tab ? Assign role
- Select roles this client should have access to
Option B: Direct Client Scope Mappings
- Clients ? Select client ? Client scopes tab
- Click on
{client-id}-dedicatedscope - Scope tab ? Assign role
- Select roles
Step 3: Verify Token Content
Use the Token Exchange or Evaluate tab to verify tokens only contain expected roles.
Best Practices
1. Always Disable Full Scope Allowed in Production
2. Principle of Least Privilege
Only grant roles that the client actually needs:
| Client | Needed Roles | Unnecessary Roles |
|---|---|---|
| Blog App | user |
admin, billing:*, hr:* |
| Billing Portal | billing:view, billing:create |
admin, hr:*, reporting:* |
| HR System | hr:view, hr:manage |
admin, billing:* |
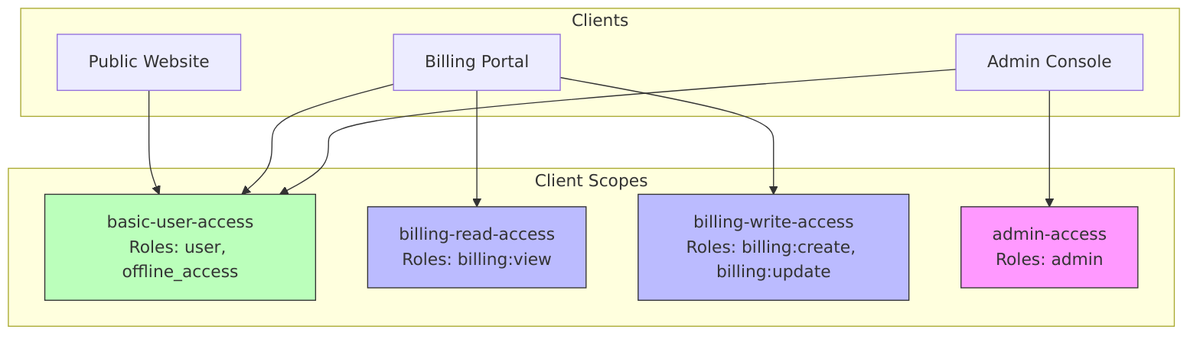
3. Use Client Scopes for Role Groups
Create reusable client scopes for common role combinations:
4. Audit Token Content Regularly
Periodically review what roles are being included in tokens:
# Get a token and decode it TOKEN=$(curl -s -X POST \ "https://keycloak.example.com/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/token" \ -d "client_id=my-client" \ -d "client_secret=secret" \ -d "username=testuser" \ -d "password=password" \ -d "grant_type=password" | jq -r '.access_token') # Decode and inspect echo $TOKEN | cut -d'.' -f2 | base64 -d | jq '.realm_access, .resource_access'
5. Use Dedicated Client Scopes
Don’t rely on default scopes for sensitive role mappings:
? Create "billing-api-access" scope with specific roles ? Add roles to the built-in "roles" scope
6. Document Role Requirements
For each client, document:
- Which roles are required
- Why each role is needed
- Which client scopes provide them
Security Implications
Risk: Over-Privileged Tokens
| Scenario | Risk | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Token theft | Attacker gains all user permissions | Disable full scope, limit roles |
| XSS attack | Malicious script accesses all APIs | Reduce token scope |
| Compromised client | All user roles exposed | Scope to client’s needs only |
| Token forwarding | Downstream service gets excessive access | Use audience restrictions + scope limits |
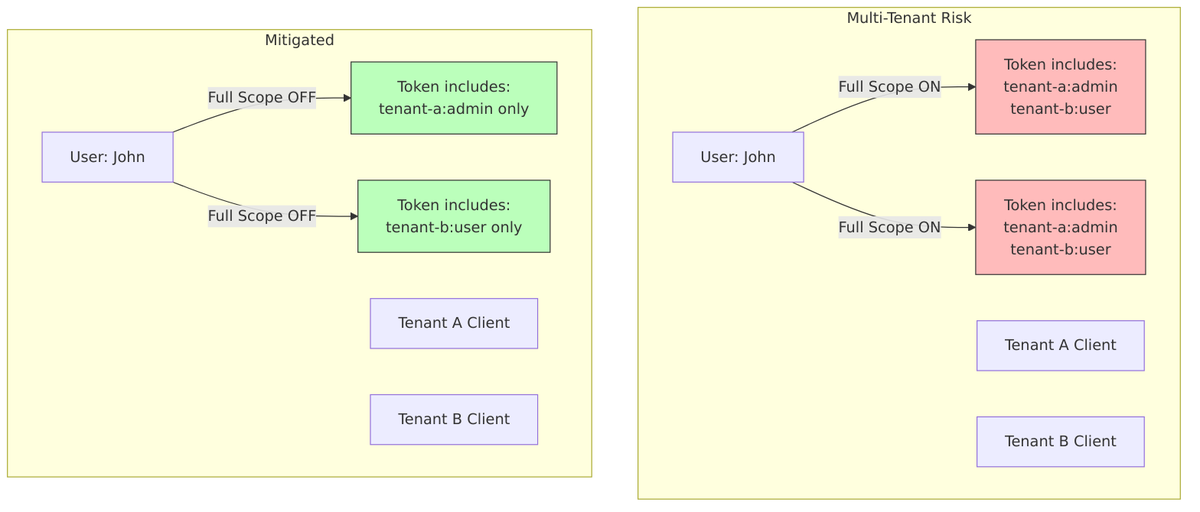
Risk: Cross-Tenant Data Access
In multi-tenant setups with shared users:
FAPI Compliance
FAPI (Financial-grade API) profiles require fullScopeAllowed = false:
From keycloak-default-client-profiles.json:
{
"name": "fapi-1-baseline",
"executors": [
{
"executor": "full-scope-disabled",
"configuration": {
"auto-configure": true
}
}
]
}
The full-scope-disabled executor:
- Automatically sets
fullScopeAllowed = falseon client registration/update - Prevents enabling full scope for FAPI-compliant clients
Database Schema
From ClientEntity.java:
-- Client table stores fullScopeAllowed flag
CREATE TABLE CLIENT (
ID VARCHAR(36) PRIMARY KEY,
CLIENT_ID VARCHAR(255),
REALM_ID VARCHAR(36),
FULL_SCOPE_ALLOWED BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
-- ... other columns
);
-- Scope mappings stored in separate table
CREATE TABLE SCOPE_MAPPING (
CLIENT_ID VARCHAR(36) NOT NULL,
ROLE_ID VARCHAR(36) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (CLIENT_ID, ROLE_ID),
FOREIGN KEY (CLIENT_ID) REFERENCES CLIENT(ID),
FOREIGN KEY (ROLE_ID) REFERENCES KEYCLOAK_ROLE(ID)
);
-- Client scope role mappings
CREATE TABLE CLIENT_SCOPE_ROLE_MAPPING (
SCOPE_ID VARCHAR(36) NOT NULL,
ROLE_ID VARCHAR(36) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (SCOPE_ID, ROLE_ID),
FOREIGN KEY (SCOPE_ID) REFERENCES CLIENT_SCOPE(ID),
FOREIGN KEY (ROLE_ID) REFERENCES KEYCLOAK_ROLE(ID)
);
Checklist for Production
- [ ] Disable
fullScopeAllowedfor all production clients - [ ] Create dedicated client scopes for role groups
- [ ] Map only required roles to each client
- [ ] Use optional scopes for elevated permissions
- [ ] Document role requirements per client
- [ ] Enable FAPI profile for financial applications
- [ ] Audit tokens regularly for scope creep
- [ ] Review scope mappings during security audits
Related Source Files
| Component | File |
|---|---|
| ClientModel Interface | ClientModel.java |
| TokenManager | TokenManager.java |
| ScopeContainerModel | ScopeContainerModel.java |
| ClientSessionContext | ClientSessionContext.java |
| DefaultClientSessionContext | DefaultClientSessionContext.java |
| RoleResolveUtil | RoleResolveUtil.java |
| FullScopeDisabledExecutor | FullScopeDisabledExecutor.java |
| ClientEntity | ClientEntity.java |