Keycloak provides comprehensive LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) integration through its User Federation system. This allows organizations to authenticate users against existing LDAP directories (such as Active Directory, OpenLDAP, or other LDAP-compliant servers) while leveraging Keycloak’s advanced identity management features.
Key Features:
- User authentication against LDAP
- User synchronization (import users to Keycloak database)
- Attribute mapping between LDAP and Keycloak
- Group and role synchronization
- Multiple edit modes (READ_ONLY, WRITABLE, UNSYNCED)
- Support for Active Directory, OpenLDAP, Red Hat Directory Server, and others
Source Code Location: federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/
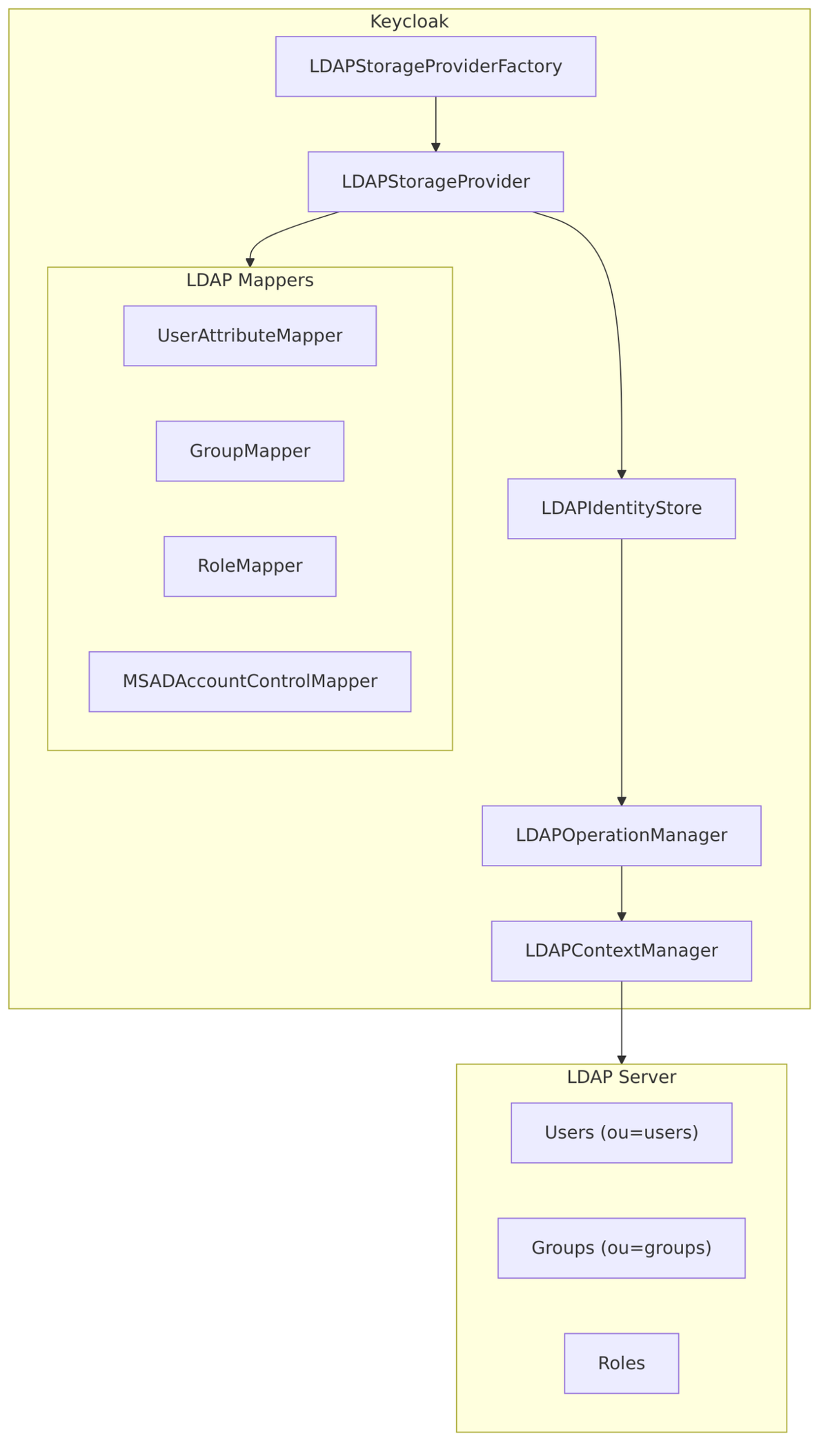
Architecture
Core Components
| Component | File | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| LDAPStorageProviderFactory | LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java | Creates providers, handles sync, manages configuration |
| LDAPStorageProvider | LDAPStorageProvider.java | Main provider for user operations |
| LDAPConfig | LDAPConfig.java | Configuration model |
| LDAPIdentityStore | LDAPIdentityStore.java | High-level LDAP operations |
| LDAPOperationManager | LDAPOperationManager.java | Low-level LDAP operations |
| LDAPContextManager | LDAPContextManager.java | JNDI connection management |
Provider Implementation
LDAPStorageProvider
The main provider implements multiple interfaces to provide full user federation capabilities:
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/LDAPStorageProvider.java
public class LDAPStorageProvider implements
UserStorageProvider, // Base storage provider
CredentialInputValidator, // Password validation
CredentialInputUpdater, // Password updates
CredentialAuthentication, // Kerberos/SPNEGO auth
UserLookupProvider, // User lookup by ID/username/email
UserRegistrationProvider, // User registration
UserQueryMethodsProvider, // User search
ImportedUserValidation, // Validate imported users
UserProfileDecorator { // Customize user profile
protected LDAPStorageProviderFactory factory;
protected KeycloakSession session;
protected UserStorageProviderModel model;
protected LDAPIdentityStore ldapIdentityStore;
protected EditMode editMode;
protected LDAPProviderKerberosConfig kerberosConfig;
protected LDAPStorageMapperManager mapperManager;
protected LDAPStorageUserManager userManager;
}
Provider Factory
The factory handles provider lifecycle, configuration, and synchronization:
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java
public class LDAPStorageProviderFactory implements
UserStorageProviderFactory<ldapstorageprovider>,
ImportSynchronization {
// Sync users from LDAP to Keycloak
@Override
public SynchronizationResult sync(KeycloakSessionFactory sessionFactory,
String realmId,
UserStorageProviderModel model) {
// Full sync - imports all LDAP users
}
@Override
public SynchronizationResult syncSince(Date lastSync,
KeycloakSessionFactory sessionFactory,
String realmId,
UserStorageProviderModel model) {
// Changed users sync - imports users modified since lastSync
}
}
Configuration
Connection Settings
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/LDAPConfig.java
public class LDAPConfig {
public static final String DEFAULT_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT = "5000";
// Connection URL (ldap:// or ldaps://)
public String getConnectionUrl() {
return config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.CONNECTION_URL);
}
// Authentication type (simple, none)
public String getAuthType() {
String value = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.AUTH_TYPE);
return value == null ? LDAPConstants.AUTH_TYPE_SIMPLE : value;
}
// Bind DN for admin connection
public String getBindDN() {
return config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.BIND_DN);
}
// Users search DN
public String getUsersDn() {
return config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.USERS_DN);
}
// User object classes
public Collection<string> getUserObjectClasses() {
String objClassesCfg = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.USER_OBJECT_CLASSES);
String objClassesStr = (objClassesCfg != null && objClassesCfg.length() > 0)
? objClassesCfg.trim()
: "inetOrgPerson,organizationalPerson";
// Parse and return as Set
}
// Edit mode
public EditMode getEditMode() {
String editModeString = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.EDIT_MODE);
return editModeString == null
? EditMode.READ_ONLY
: EditMode.valueOf(editModeString);
}
// Vendor-specific settings
public boolean isActiveDirectory() {
String vendor = getVendor();
return vendor != null && vendor.equals(LDAPConstants.VENDOR_ACTIVE_DIRECTORY);
}
}
Configuration Properties
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
connectionUrl |
LDAP server URL (ldap://host:389 or ldaps://host:636) | Required |
bindDn |
DN of admin user for LDAP operations | Required |
bindCredential |
Password for bind DN | Required |
usersDn |
Base DN for user searches | Required |
userObjectClasses |
Object classes for user entries | inetOrgPerson,organizationalPerson |
usernameLDAPAttribute |
LDAP attribute for username | uid (or sAMAccountName for AD) |
rdnLDAPAttribute |
RDN attribute for user entries | uid |
uuidLDAPAttribute |
UUID attribute for unique identification | entryUUID (or objectGUID for AD) |
editMode |
Edit mode (READ_ONLY, WRITABLE, UNSYNCED) | READ_ONLY |
vendor |
LDAP vendor for vendor-specific behavior | Auto-detected |
searchScope |
Search scope (1=one level, 2=subtree) | 2 (subtree) |
connectionPooling |
Enable JNDI connection pooling | true |
connectionTimeout |
Connection timeout in milliseconds | 5000 |
readTimeout |
Read timeout in milliseconds | None |
startTls |
Use StartTLS for encryption | false |
pagination |
Enable paged results | true |
batchSizeForSync |
Page size for sync operations | 1000 |
LDAP Searching and Updating
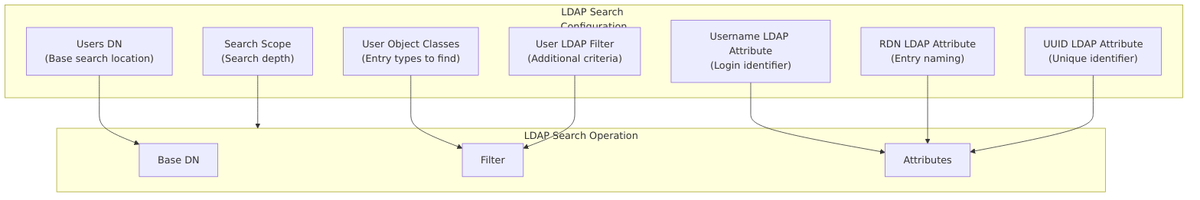
This section covers the core configuration options that control how Keycloak searches for users in LDAP and how user data is updated. These settings are critical for proper integration and performance.
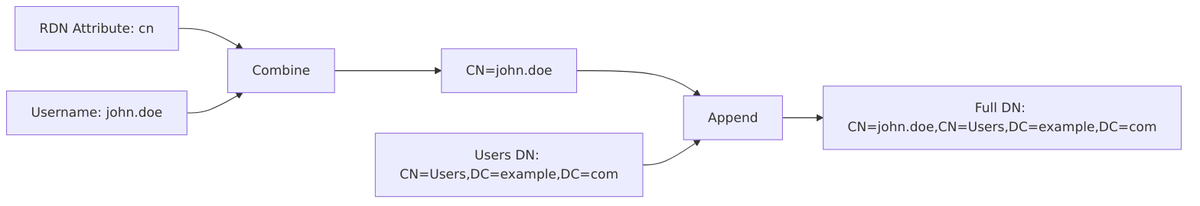
Users DN
The Users DN (Distinguished Name) specifies the base location in the LDAP directory tree where Keycloak will search for user entries.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:217-219:
public String getUsersDn() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.USERS_DN);
return str;
}
Configuration Examples:
| LDAP Vendor | Example Users DN |
|---|---|
| Active Directory | CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com |
| OpenLDAP | ou=People,dc=example,dc=com |
| FreeIPA | cn=users,cn=accounts,dc=example,dc=com |
| 389 Directory | ou=People,dc=example,dc=com |
Important Considerations:
- This DN must exist in your LDAP directory
- Users are searched within this subtree (or at this level, depending on search scope)
- For Active Directory, common locations include:
CN=Users,DC=domain,DC=com– default Users containerOU=MyUsers,DC=domain,DC=com– custom organizational unit
Username LDAP Attribute
The Username LDAP Attribute is the LDAP attribute that maps to the Keycloak username. This is the attribute users will use to log in.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:221-224:
public String getUsernameLdapAttribute() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.USERNAME_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE);
return str;
}
Vendor-Specific Defaults:
| LDAP Vendor | Default Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | sAMAccountName or cn |
Pre-Windows 2000 logon name |
| OpenLDAP | uid |
Unix user identifier |
| FreeIPA | uid |
User login name |
| 389 Directory | uid |
Standard uid attribute |
| Other | uid |
Generic default |
Example Configuration for Active Directory:
Username LDAP attribute: cn
When a user logs in with username “john.doe”, Keycloak searches:
RDN LDAP Attribute
The RDN (Relative Distinguished Name) LDAP Attribute is the attribute used to construct the DN of new user entries created in LDAP.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:226-229:
public String getRdnLdapAttribute() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.RDN_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE);
return str;
}
Common Values:
| Attribute | When to Use |
|---|---|
cn |
Active Directory (common name) |
uid |
UNIX-based LDAP (OpenLDAP, 389 DS) |
sAMAccountName |
AD alternative |
UUID LDAP Attribute
The UUID LDAP Attribute is the unique identifier for each LDAP entry. This is critical for tracking users even if their DN changes (e.g., user moves to different OU, name change).
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:231-242:
public String getUuidLDAPAttributeName() {
String uuidAttrName = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.UUID_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE);
if (uuidAttrName == null) {
// Vendor-specific default
uuidAttrName = isActiveDirectory() ?
LDAPConstants.OBJECT_GUID : LDAPConstants.ENTRY_UUID;
}
return uuidAttrName;
}
Vendor-Specific UUID Attributes:
| LDAP Vendor | UUID Attribute | Format |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | objectGUID |
Binary GUID (16 bytes) |
| OpenLDAP | entryUUID |
RFC 4122 UUID string |
| FreeIPA | ipaUniqueID or nsUniqueId |
UUID string |
| 389 Directory | nsUniqueId |
Netscape unique ID |
| eDirectory | GUID |
Novell GUID |
Example for Active Directory:
UUID LDAP attribute: objectGUID
Why UUID Matters:
- User renames:
CN=John Doe?CN=John Smith– UUID stays same - User moves:
OU=Sales?OU=Marketing– UUID stays same - Keycloak uses UUID to maintain relationship between Keycloak user and LDAP entry
User Object Classes
User Object Classes define which LDAP object classes are used to identify user entries. Keycloak uses these to:
- Build search filters when looking for users
- Set object classes when creating new users (in WRITABLE mode)
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:244-250:
public Collection<string> getUserObjectClasses() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.USER_OBJECT_CLASSES);
if (str == null || str.isEmpty()) {
str = "inetOrgPerson, organizationalPerson";
}
return parseMultivaluedString(str);
}
Common Configurations:
| LDAP Vendor | Object Classes |
|---|---|
| Active Directory | person, organizationalPerson, user |
| OpenLDAP | inetOrgPerson, organizationalPerson |
| FreeIPA | inetOrgPerson, posixAccount |
| 389 Directory | inetOrgPerson, organizationalPerson |
How Object Classes Build the Search Filter:
For configuration:
User object classes: person, organizationalPerson, user
Keycloak builds filter:
User LDAP Filter
The User LDAP Filter is an optional additional LDAP filter to further restrict which users are found. This is combined (AND) with the object class filter.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:252-255:
public String getCustomUserSearchFilter() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.CUSTOM_USER_SEARCH_FILTER);
return str;
}
Example Filters:
| Use Case | Filter |
|---|---|
| Only enabled accounts (AD) | (!(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=2)) |
| Members of group | (memberOf=CN=KeycloakUsers,OU=Groups,DC=example,DC=com) |
| Specific department | (department=IT) |
| Email domain | (mail=*@company.com) |
| Multiple conditions | (&(department=IT)(!(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=2))) |
Combined Filter Example:
Object classes: person, organizationalPerson, user
Custom filter: (memberOf=CN=KeycloakUsers,OU=Groups,DC=example,DC=com)
Final search filter:
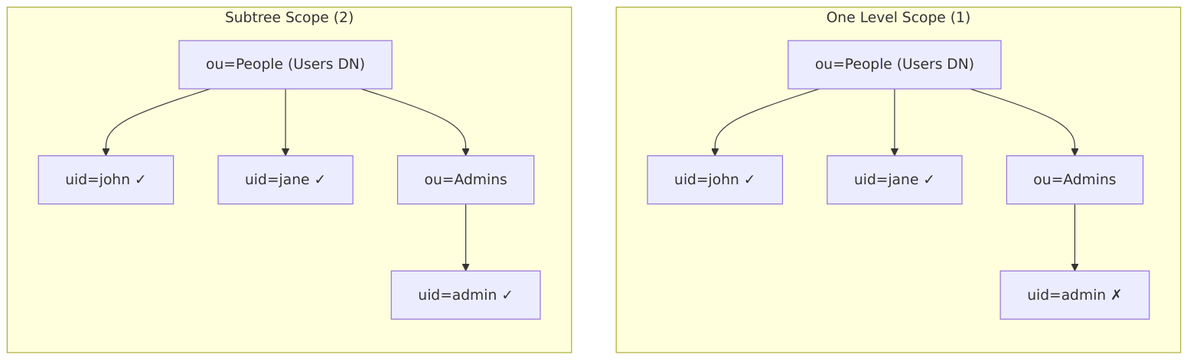
Search Scope
Search Scope determines how deep Keycloak searches within the Users DN.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:257-268:
public int getSearchScope() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.SEARCH_SCOPE);
if (str == null) {
return SearchControls.SUBTREE_SCOPE; // Default: 2
}
return Integer.parseInt(str);
}
Scope Values:
| Value | Constant | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 |
ONELEVEL_SCOPE |
Search only immediate children of Users DN |
2 |
SUBTREE_SCOPE |
Search entire subtree under Users DN (default) |
When to Use Each:
| Scope | Use Case |
|---|---|
| One Level | Flat user structure, better performance, explicit control |
| Subtree | Users in nested OUs, complex directory structure |
Read Timeout
Read Timeout specifies the maximum time (in milliseconds) to wait for LDAP read operations.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:270-278:
public int getReadTimeout() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.READ_TIMEOUT);
if (str == null) {
return 0; // No timeout (default)
}
return Integer.parseInt(str);
}
Recommendations:
| Scenario | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Local/Fast LDAP | 5000 (5 seconds) |
| Remote LDAP | 30000 (30 seconds) |
| Slow network | 60000 (60 seconds) |
| No timeout | Not set or 0 |
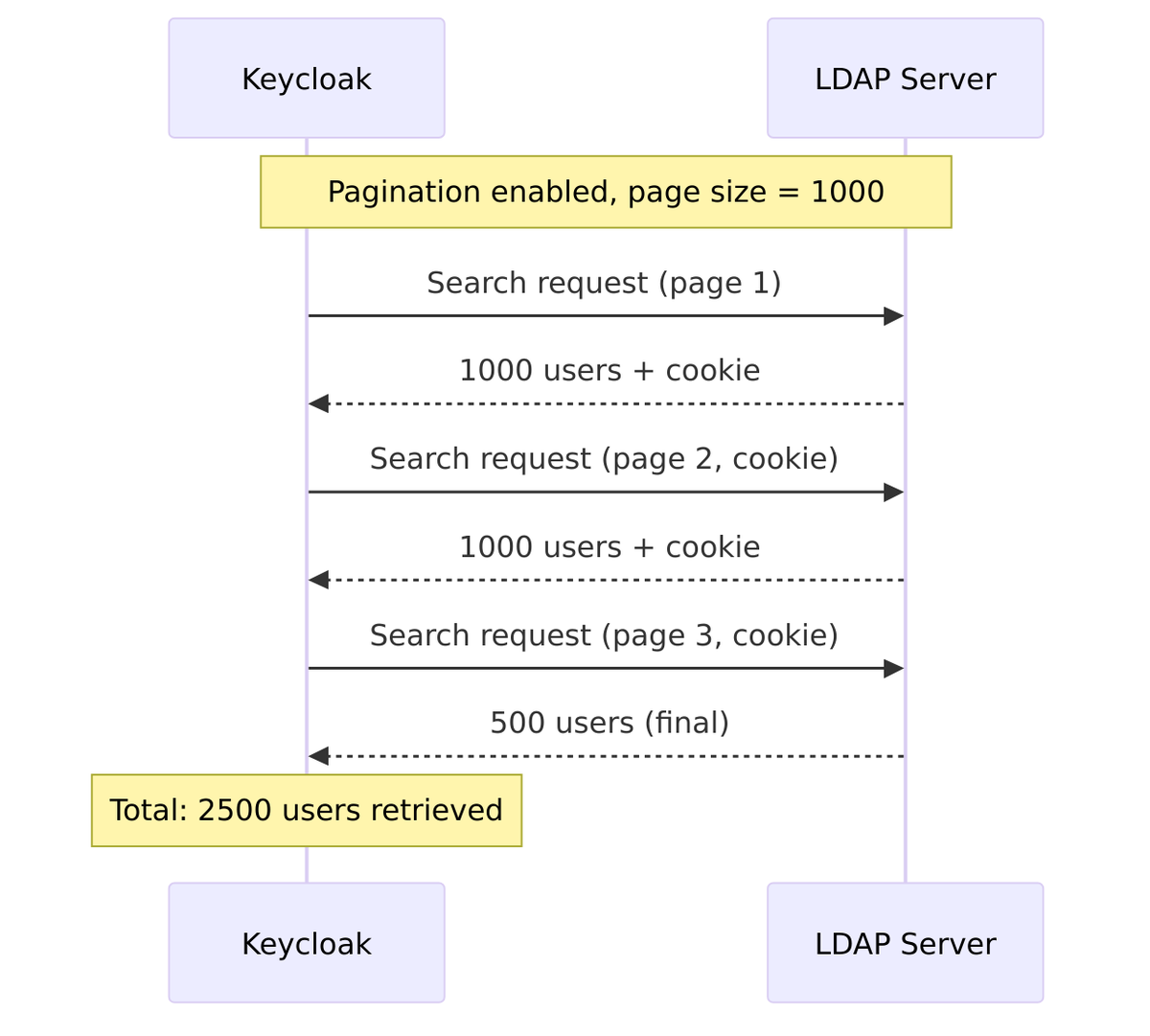
Pagination
Pagination enables paged results control for large directories. This is essential when the LDAP server has limits on result size.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:280-286:
public boolean isPagination() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.PAGINATION);
return str != null && Boolean.parseBoolean(str);
}
Why Pagination is Important:
- Most LDAP servers limit results (AD default: 1000)
- Without pagination, only first N users returned
- Essential for directories with more than ~1000 users
Page Size Configuration:
Pagination: On Batch Size For Sync: 1000 (default)
Referral
Referral handling controls how Keycloak responds when the LDAP server returns a referral to another server.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:288-294:
public String getReferral() {
String str = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.REFERRAL);
if (str == null) {
return "ignore"; // Default
}
return str;
}
Referral Options:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
ignore |
Ignore referrals (default, recommended for most cases) |
follow |
Automatically follow referrals to other servers |
throw |
Throw exception when referral encountered |
When to Use follow:
- Multi-domain Active Directory forests
- Distributed LDAP topology
- Global catalog searches
Caution with follow:
- May cause performance issues
- Requires network access to referred servers
- Can lead to authentication failures if credentials not valid on referred server
Configuration Summary Table
| Setting | Example Value (AD) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Users DN | CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com |
Where to search |
| Username LDAP attribute | cn |
Login identifier |
| RDN LDAP attribute | cn |
DN construction |
| UUID LDAP attribute | objectGUID |
Unique ID tracking |
| User object classes | person, organizationalPerson, user |
Entry type filter |
| User LDAP filter | (memberOf=CN=App,...) |
Additional filtering |
| Search scope | One Level or Subtree |
Search depth |
| Read timeout | 30000 |
Operation timeout |
| Pagination | On |
Handle large directories |
| Referral | ignore |
Cross-server references |
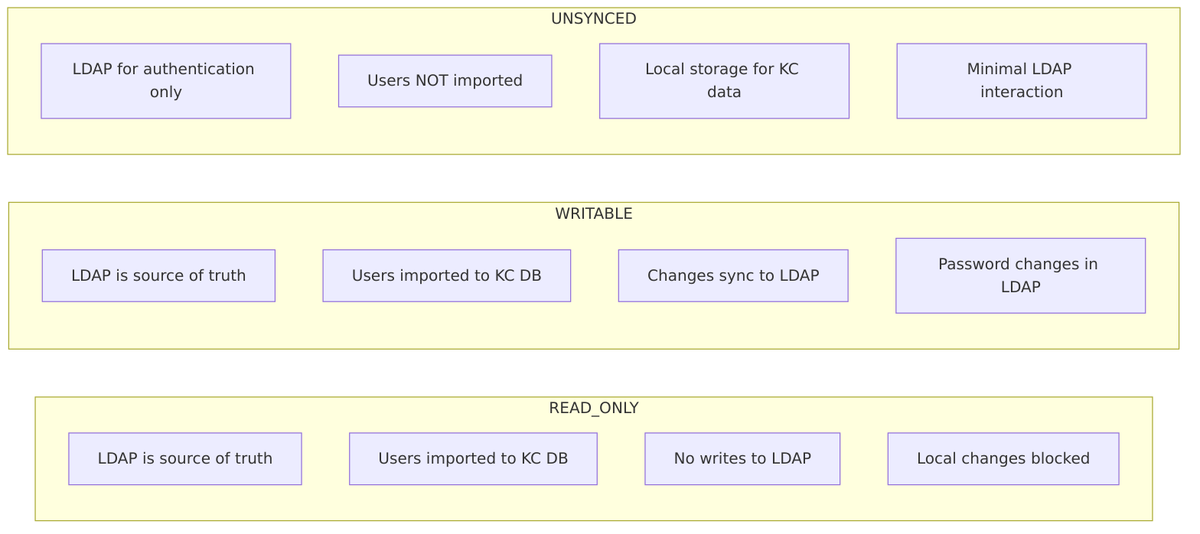
Edit Modes
Keycloak supports three edit modes that control how user data is synchronized:
READ_ONLY Mode
Users are imported from LDAP but cannot be modified:
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/ReadonlyLDAPUserModelDelegate.java
public class ReadonlyLDAPUserModelDelegate extends UserModelDelegate {
@Override
public void setUsername(String username) {
if (getUsername().equals(username)) {
// Same value - allowed (idempotent)
return;
}
throw new ReadOnlyException("User is read-only");
}
@Override
public void setSingleAttribute(String name, String value) {
if (value.equals(getFirstAttribute(name))) {
return;
}
throw new ReadOnlyException("User is read-only");
}
}
WRITABLE Mode
Changes to users are synchronized back to LDAP:
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/LDAPWritesOnlyUserModelDelegate.java
public class LDAPWritesOnlyUserModelDelegate extends UserModelDelegate {
private final LDAPTransaction ldapTransaction;
private final LDAPObject ldapObject;
@Override
public void setSingleAttribute(String name, String value) {
// Track which attributes are updated
ldapTransaction.addUpdatedAttribute(name);
delegate.setSingleAttribute(name, value);
}
}
// Transaction commits changes to LDAP
public class LDAPTransaction {
@Override
protected void commitImpl() {
if (!updatedAttributes.isEmpty()) {
// Commit changes to LDAP
ldapIdentityStore.update(ldapObject);
}
}
}
UNSYNCED Mode
Users are not imported; LDAP is used only for authentication:
// In LDAPStorageProvider.proxy()
if (model.isImportEnabled()) {
// Import mode - store users in local DB
return proxiedUser;
} else {
// No import - use in-memory adapter
return new InMemoryUserAdapter(session, realm, storageId);
}
User Synchronization
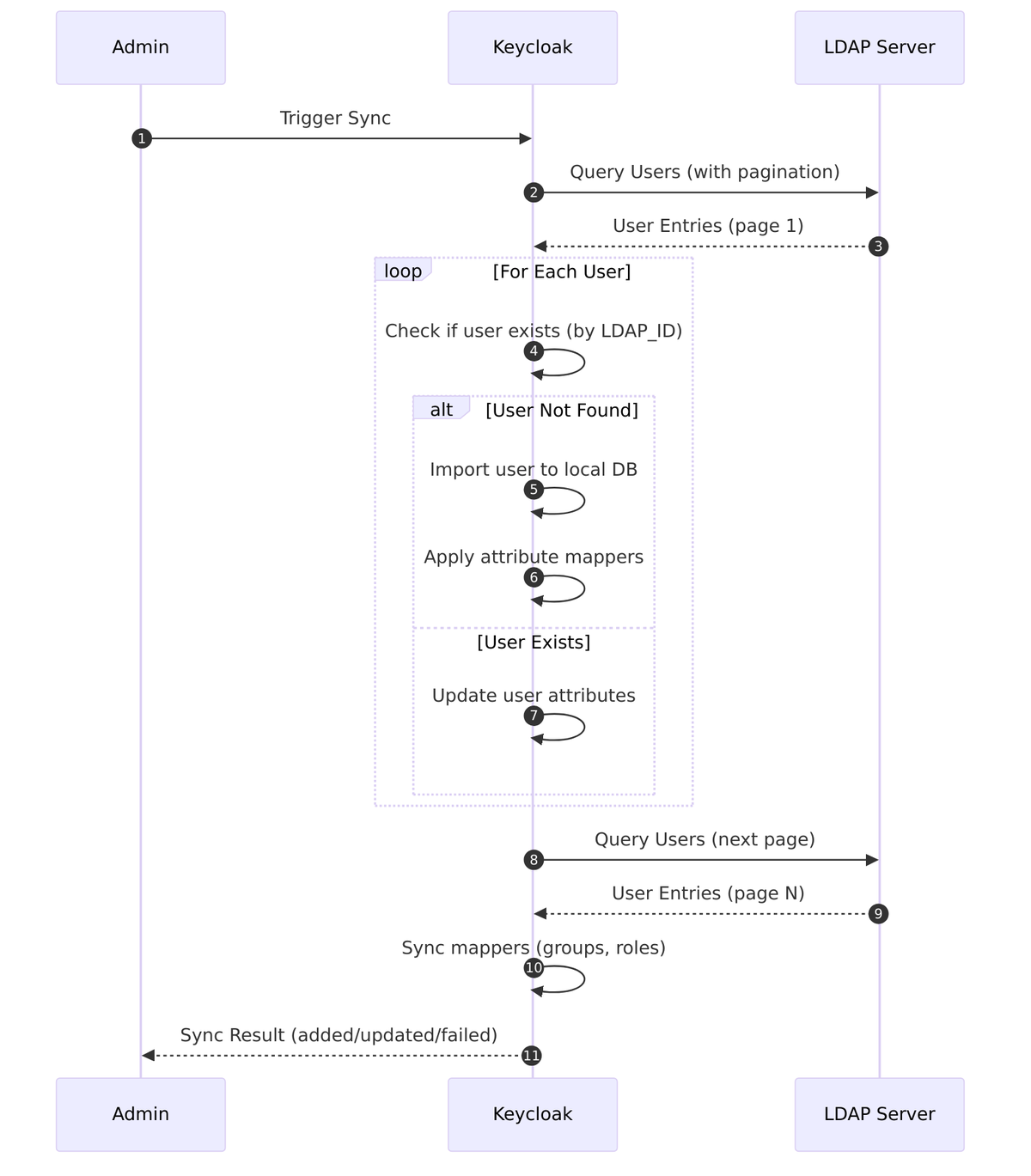
Sync Flow
Sync Implementation
// LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java
@Override
public SynchronizationResult sync(KeycloakSessionFactory sessionFactory,
String realmId,
UserStorageProviderModel model) {
// Create LDAP query for all users
try (LDAPQuery query = createQuery(ldapProvider, realm, model)) {
SynchronizationResult result = new SynchronizationResult();
// Process users in batches with pagination
boolean hasNext = true;
while (hasNext) {
List<ldapobject> ldapUsers = query.getResultList();
for (LDAPObject ldapUser : ldapUsers) {
try {
importLdapUser(session, realm, ldapProvider, ldapUser, result);
} catch (ModelException e) {
result.increaseFailed();
}
}
hasNext = query.hasMorePages();
if (hasNext) {
query.nextPage();
}
}
// Sync mapper-specific data (groups, roles)
syncMappers(sessionFactory, realmId, model, result);
return result;
}
}
private void importLdapUser(KeycloakSession session, RealmModel realm,
LDAPStorageProvider ldapProvider,
LDAPObject ldapUser,
SynchronizationResult result) {
String ldapId = ldapUser.getUuid();
String username = LDAPUtils.getUsername(ldapUser, ldapProvider.getLdapIdentityStore().getConfig());
// Check if user already exists
UserModel existingUser = session.users().getUserByFederatedIdentity(realm,
new FederatedIdentityModel(model.getId(), ldapId, username));
if (existingUser == null) {
// Import new user
UserModel imported = ldapProvider.importUserFromLDAP(session, realm, ldapUser);
result.increaseAdded();
} else {
// Update existing user
ldapProvider.updateImportedUser(session, realm, existingUser, ldapUser);
result.increaseUpdated();
}
}
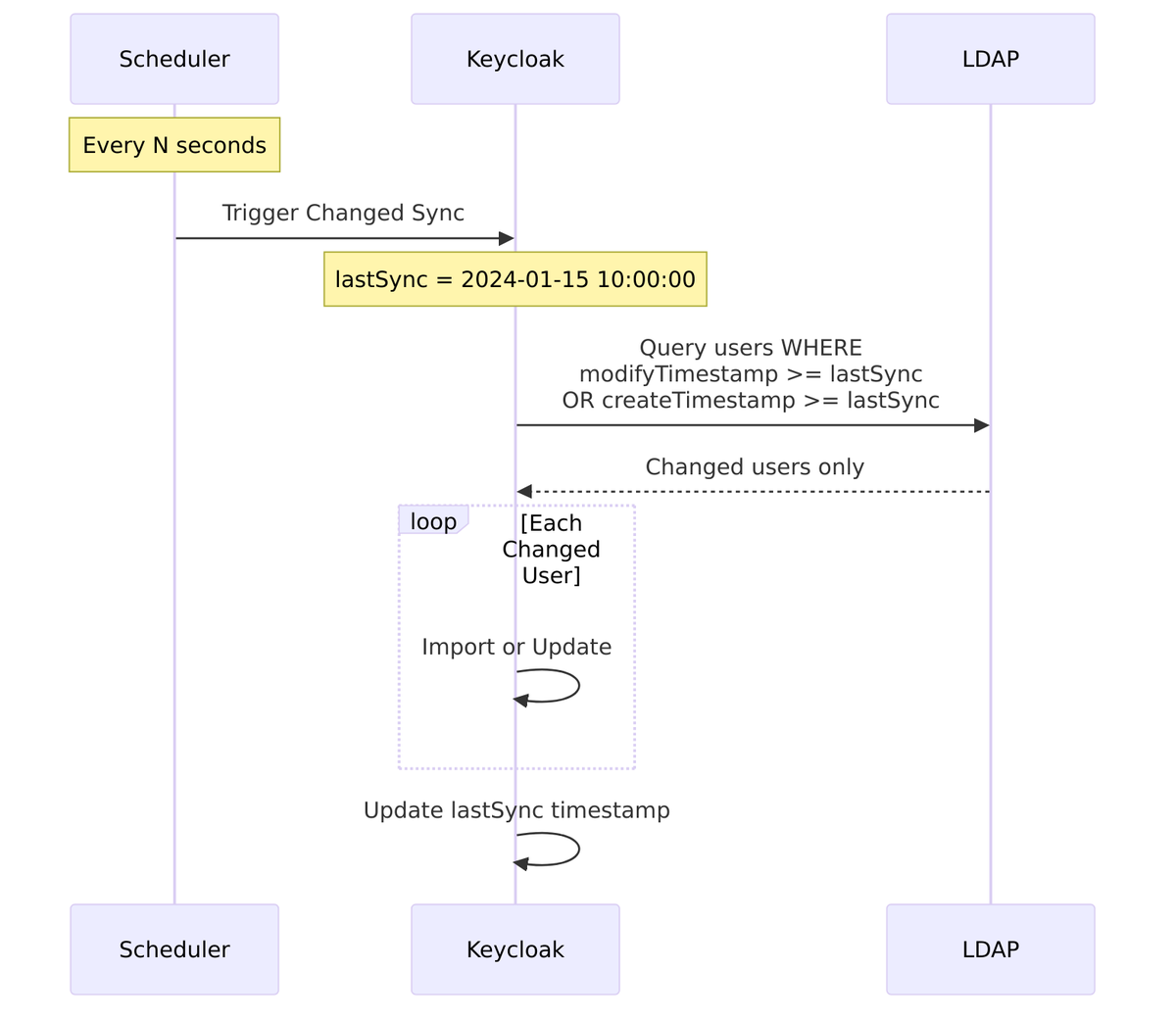
Sync Since (Changed Users)
For incremental sync, Keycloak uses modification timestamps:
@Override
public SynchronizationResult syncSince(Date lastSync,
KeycloakSessionFactory sessionFactory,
String realmId,
UserStorageProviderModel model) {
// Add filter for users modified since lastSync
LDAPQueryConditionsBuilder conditionsBuilder = new LDAPQueryConditionsBuilder();
// Different attributes for different LDAP vendors
String modifyTimestampAttr = ldapConfig.isActiveDirectory()
? "whenChanged"
: "modifyTimestamp";
Condition condition = conditionsBuilder.greaterThanOrEqual(
modifyTimestampAttr,
LDAPUtils.formatDate(lastSync)
);
query.addWhereCondition(condition);
return syncImpl(sessionFactory, realmId, model, query);
}
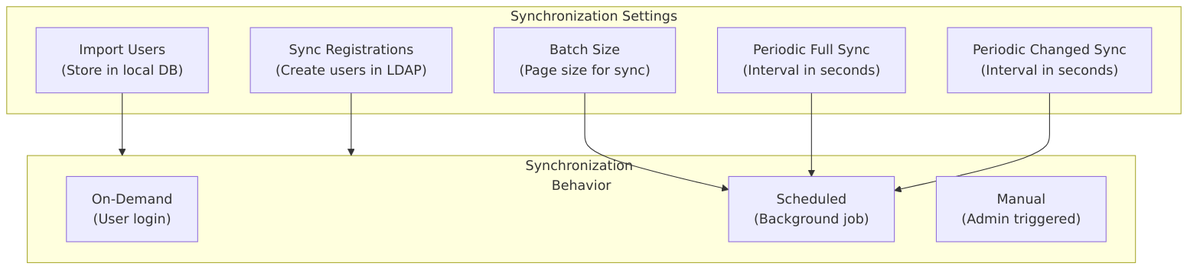
Synchronization Settings
This section covers the configuration options that control how and when Keycloak synchronizes users between LDAP and its local database.
Import Users
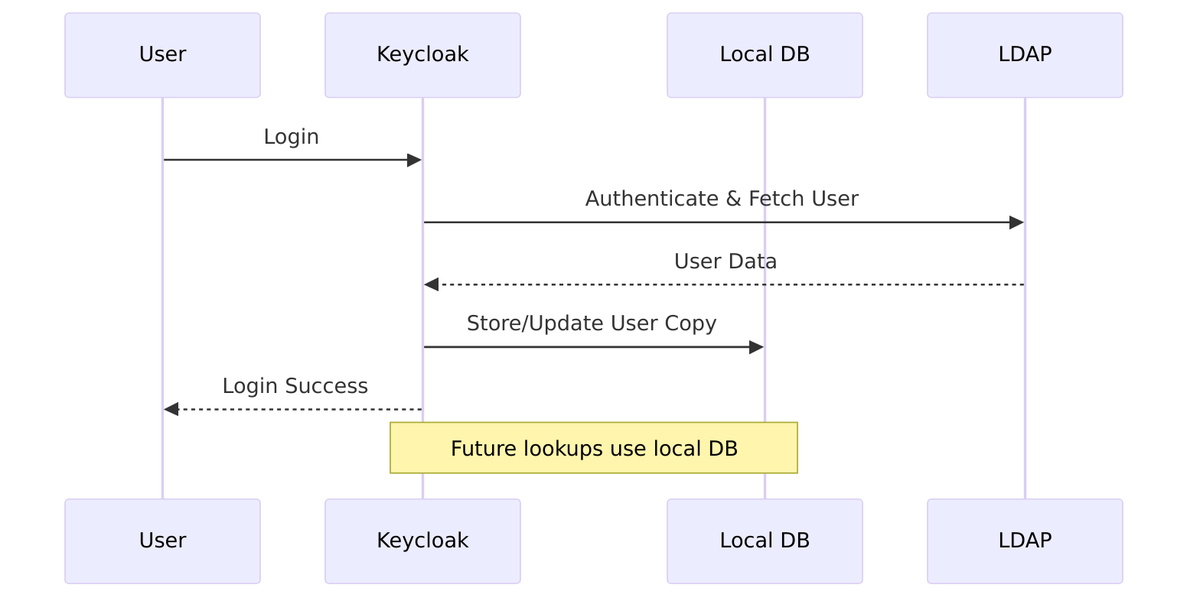
Import Users controls whether users are stored in Keycloak’s local database when they are found in LDAP.
Source Code Reference – UserStorageProviderModel.java:56-61:
public static final String IMPORT_ENABLED = "importEnabled";
public boolean isImportEnabled() {
if (importEnabled == null) {
importEnabled = Boolean.parseBoolean(
getConfig().getFirstOrDefault(IMPORT_ENABLED, Boolean.TRUE.toString()));
}
return importEnabled;
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| On (default) | Users are copied to Keycloak’s local database. Faster lookups, enables local features. |
| Off | Users remain only in LDAP. Every operation requires LDAP query. Minimal local storage. |
When Import is OFF:
// LDAPStorageProvider.addUser()
if (model.isImportEnabled()) {
user = UserStoragePrivateUtil.userLocalStorage(session).addUser(realm, username);
user.setFederationLink(model.getId());
} else {
// In-memory only, no persistence
user = new InMemoryUserAdapter(session, realm, storageId);
user.setUsername(username);
}
Considerations:
- Import ON: Better performance, supports offline access, enables complex queries
- Import OFF: Reduces database size, always reflects current LDAP state, suitable for very large directories
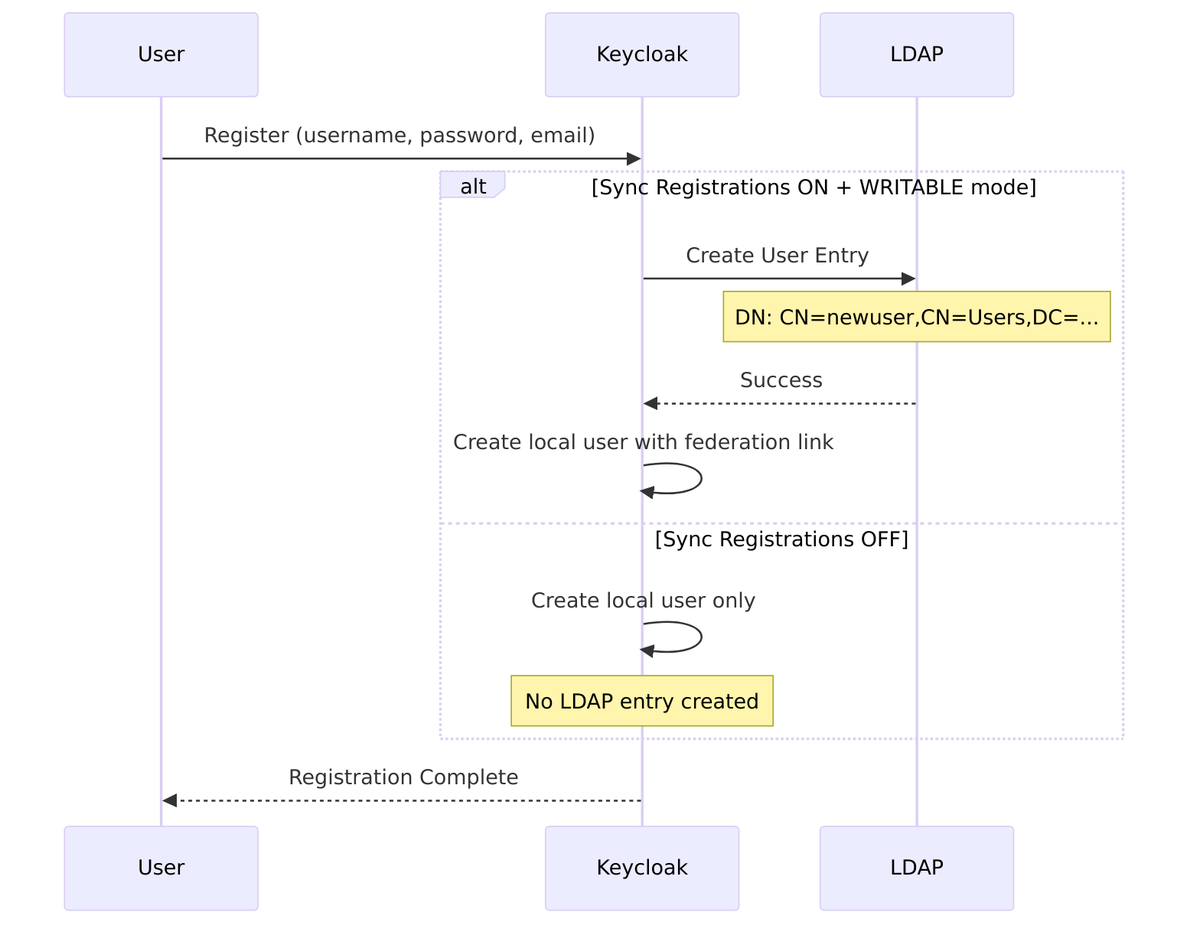
Sync Registrations
Sync Registrations controls whether users registered in Keycloak are automatically created in LDAP.
Source Code Reference – LDAPStorageProvider.java:314-316:
public boolean synchronizeRegistrations() {
return "true".equalsIgnoreCase(model.getConfig().getFirst(LDAPConstants.SYNC_REGISTRATIONS))
&& editMode == UserStorageProvider.EditMode.WRITABLE;
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| On | New users registered in Keycloak are created in LDAP |
| Off (default) | Registration creates users only in Keycloak’s local database |
Requirements for Sync Registrations:
- Edit Mode must be WRITABLE (not READ_ONLY or UNSYNCED)
- LDAP must allow user creation with configured bind credentials
Source Code – User creation in LDAP – LDAPStorageProvider.java:319-329:
@Override
public UserModel addUser(RealmModel realm, String username) {
if (!synchronizeRegistrations()) {
return null; // Don't handle registration
}
final UserModel user;
if (model.isImportEnabled()) {
user = UserStoragePrivateUtil.userLocalStorage(session).addUser(realm, username);
user.setFederationLink(model.getId());
} else {
user = new InMemoryUserAdapter(session, realm, storageId);
user.setUsername(username);
}
// ... create LDAP entry
}
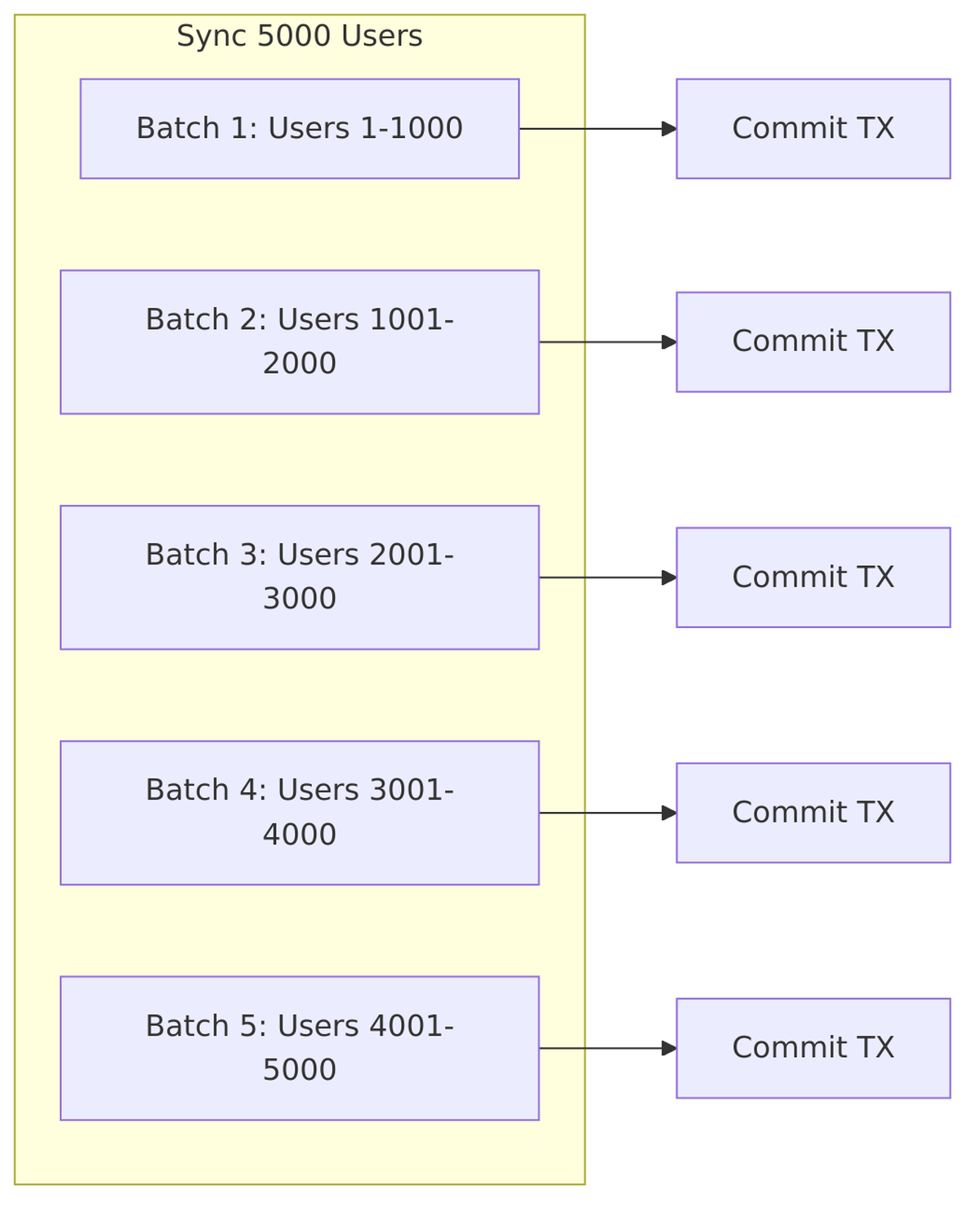
Batch Size
Batch Size (also called “Batch Size For Sync”) controls how many users are processed in a single transaction during synchronization.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConstants.java:87-88:
public static final String BATCH_SIZE_FOR_SYNC = "batchSizeForSync"; public static final int DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE_FOR_SYNC = 1000;
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Default | 1000 users per batch |
| Purpose | Controls memory usage and transaction size during sync |
How Batch Size Works:
Source Code – Batch processing – LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java:594-610:
protected SynchronizationResult syncImpl(KeycloakSessionFactory sessionFactory,
LDAPQuery userQuery,
String realmId,
ComponentModel fedModel) {
SynchronizationResult syncResult = new SynchronizationResult();
LDAPConfig ldapConfig = new LDAPConfig(fedModel.getConfig());
boolean pagination = ldapConfig.isPagination();
if (pagination) {
int pageSize = ldapConfig.getBatchSizeForSync(); // Use batch size
boolean nextPage = true;
while (nextPage) {
userQuery.setLimit(pageSize);
List<ldapobject> users = userQuery.getResultList();
nextPage = userQuery.getPaginationContext().hasNextPage();
SynchronizationResult currentPageSync = importLdapUsers(..., users);
syncResult.add(currentPageSync);
}
}
return syncResult;
}
Tuning Recommendations:
| Directory Size | Recommended Batch Size |
|---|---|
| Small (< 1000 users) | 1000 (default) |
| Medium (1000-10000) | 500-1000 |
| Large (> 10000) | 100-500 (reduce memory pressure) |
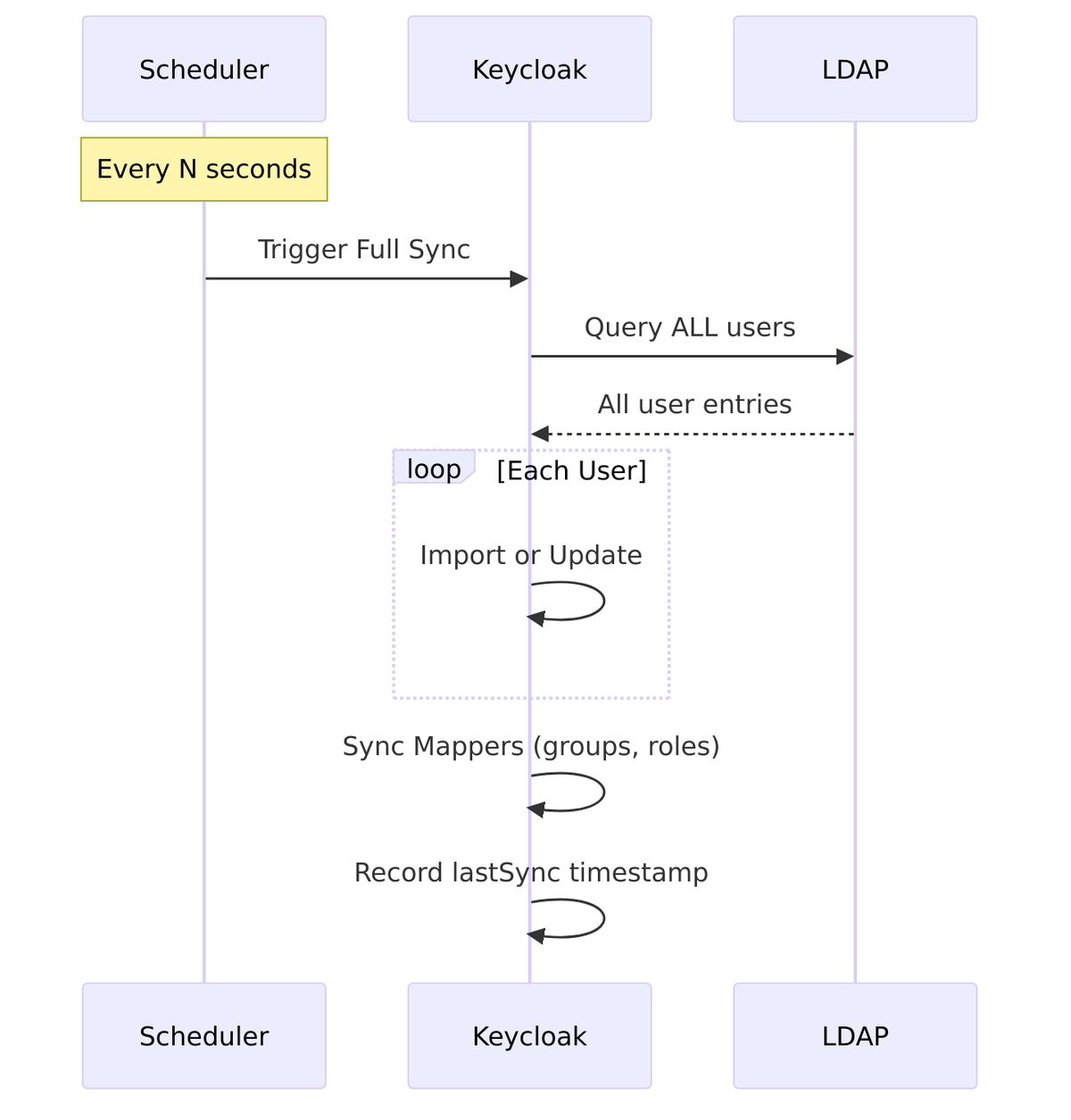
Periodic Full Sync
Periodic Full Sync schedules automatic synchronization of ALL users from LDAP at regular intervals.
Source Code Reference – UserStorageProviderModel.java:69-79:
public static final String FULL_SYNC_PERIOD = "fullSyncPeriod";
public int getFullSyncPeriod() {
if (fullSyncPeriod == null) {
String val = getConfig().getFirst(FULL_SYNC_PERIOD);
if (val == null) {
fullSyncPeriod = -1; // Disabled
} else {
fullSyncPeriod = Integer.valueOf(val);
}
}
return fullSyncPeriod;
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| -1 or empty | Disabled (no periodic sync) |
| Positive integer | Sync interval in seconds |
Example Values:
| Setting | Interval |
|---|---|
3600 |
Every 1 hour |
86400 |
Every 24 hours |
604800 |
Every 7 days |
What Full Sync Does:
- Queries ALL users matching the configured filter
- Imports new users not yet in Keycloak
- Updates existing users with current LDAP values
- Syncs mapper data (groups, roles)
Periodic Changed Users Sync
Periodic Changed Users Sync schedules automatic synchronization of only users that have changed since the last sync.
Source Code Reference – UserStorageProviderModel.java:86-96:
public static final String CHANGED_SYNC_PERIOD = "changedSyncPeriod";
public int getChangedSyncPeriod() {
if (changedSyncPeriod == null) {
String val = getConfig().getFirst(CHANGED_SYNC_PERIOD);
if (val == null) {
changedSyncPeriod = -1; // Disabled
} else {
changedSyncPeriod = Integer.valueOf(val);
}
}
return changedSyncPeriod;
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| -1 or empty | Disabled (no periodic changed sync) |
| Positive integer | Sync interval in seconds |
How Changed Sync Works:
Source Code – Changed sync filter – LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java:547-564:
@Override
public SynchronizationResult syncSince(Date lastSync,
KeycloakSessionFactory sessionFactory,
String realmId,
UserStorageProviderModel model) {
LDAPQueryConditionsBuilder conditionsBuilder = new LDAPQueryConditionsBuilder();
// Filter: createTimestamp >= lastSync OR modifyTimestamp >= lastSync
Condition createCondition = conditionsBuilder.greaterThanOrEqualTo(
LDAPConstants.CREATE_TIMESTAMP, lastSync);
Condition modifyCondition = conditionsBuilder.greaterThanOrEqualTo(
LDAPConstants.MODIFY_TIMESTAMP, lastSync);
Condition orCondition = conditionsBuilder.orCondition(createCondition, modifyCondition);
userQuery.addWhereCondition(orCondition);
return syncImpl(sessionFactory, userQuery, realmId, model);
}
LDAP Timestamp Attributes:
| Vendor | Create Timestamp | Modify Timestamp |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | whenCreated |
whenChanged |
| OpenLDAP | createTimestamp |
modifyTimestamp |
| 389 Directory | createTimestamp |
modifyTimestamp |
Sync Configuration Summary
| Setting | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Import Users | On |
Store users in local database |
| Sync Registrations | On |
Create registered users in LDAP (requires WRITABLE mode) |
| Batch Size | 1000 |
Users per sync transaction |
| Periodic Full Sync | Off (-1) |
No scheduled full sync |
| Periodic Changed Users Sync | Off (-1) |
No scheduled incremental sync |
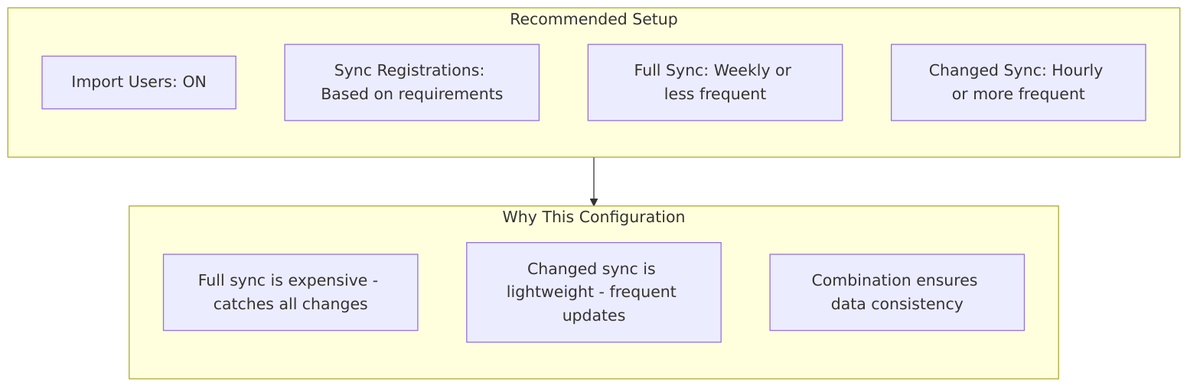
Typical Configurations:
| Scenario | Import | Sync Reg | Full Sync | Changed Sync |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read-only LDAP | On | Off | Daily | Hourly |
| Writable LDAP | On | On | Weekly | Hourly |
| No Import (live query) | Off | Off | N/A | N/A |
| Large directory (100k+) | On | Off | Weekly | Every 15 min |
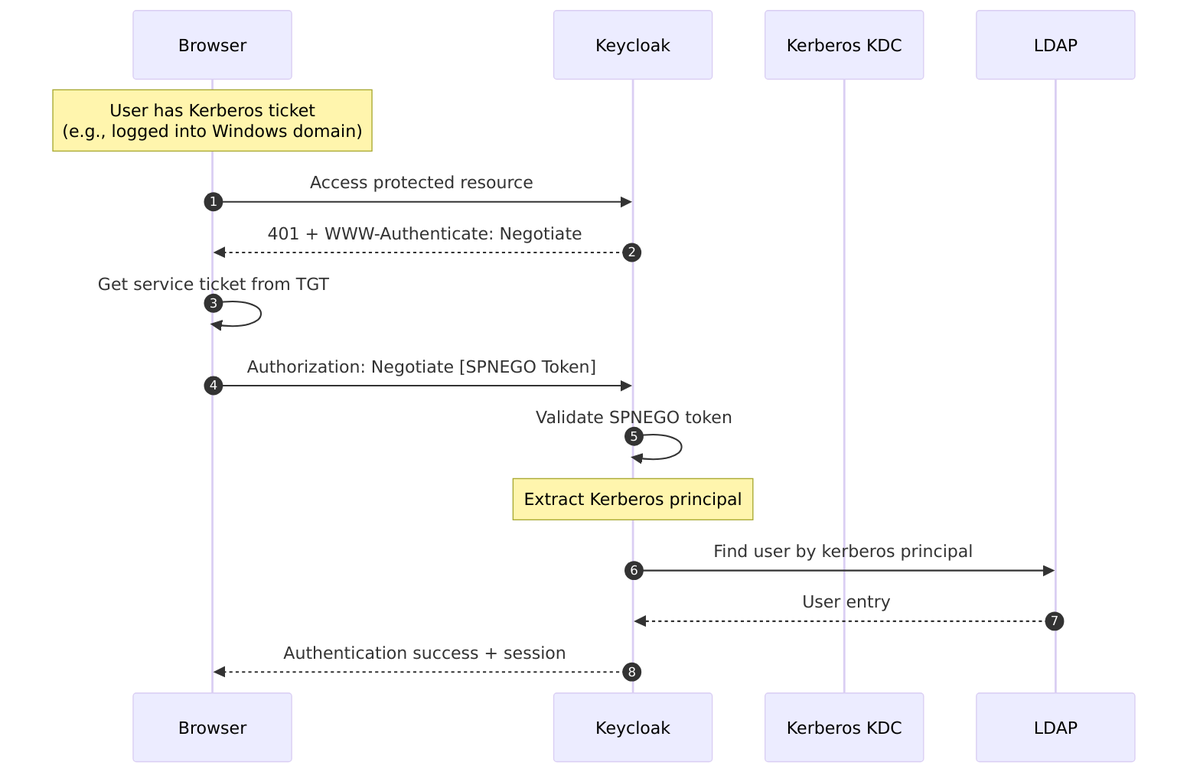
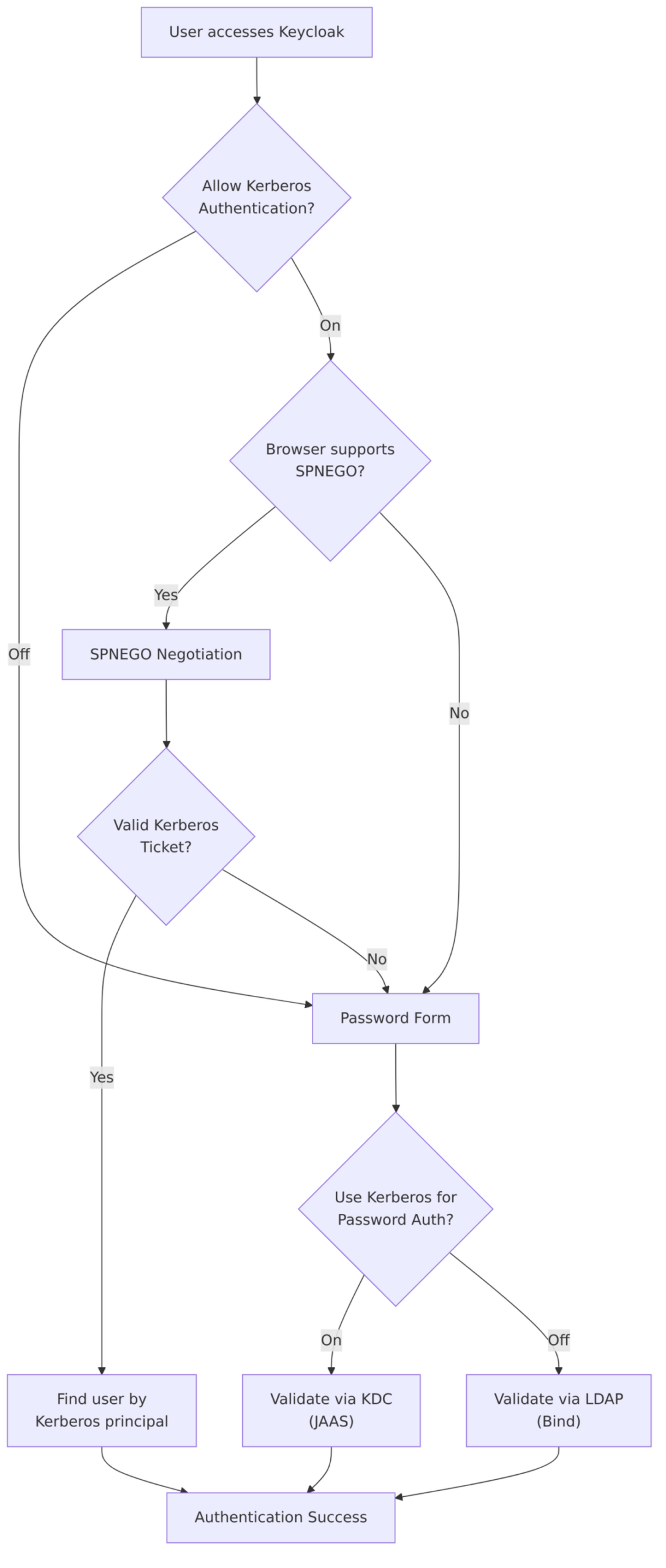
Kerberos Integration
Keycloak’s LDAP federation supports Kerberos/SPNEGO authentication, allowing users to authenticate using their Kerberos tickets (Single Sign-On) instead of passwords. This is particularly useful in Active Directory environments.
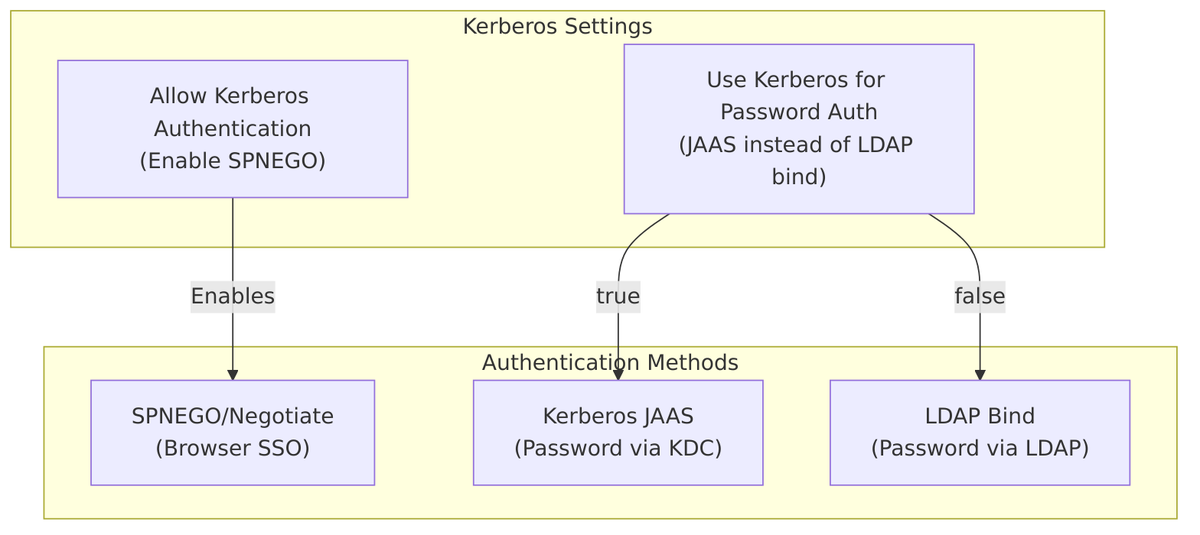
Allow Kerberos Authentication
Allow Kerberos Authentication enables SPNEGO (Simple and Protected GSSAPI Negotiation Mechanism) authentication, allowing users with valid Kerberos tickets to authenticate without entering a password.
Source Code Reference – CommonKerberosConfig.java:47-49:
public static final String ALLOW_KERBEROS_AUTHENTICATION = "allowKerberosAuthentication";
public boolean isAllowKerberosAuthentication() {
return Boolean.valueOf(getConfig().getFirst(KerberosConstants.ALLOW_KERBEROS_AUTHENTICATION));
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Off (default) | SPNEGO/Kerberos authentication disabled |
| On | SPNEGO authentication enabled for users with valid Kerberos tickets |
When Enabled:
Source Code – SPNEGO credential support – LDAPStorageProvider.java:154-156:
supportedCredentialTypes.add(PasswordCredentialModel.TYPE);
if (kerberosConfig.isAllowKerberosAuthentication()) {
supportedCredentialTypes.add(UserCredentialModel.KERBEROS);
}
Source Code – SPNEGO authentication – LDAPStorageProvider.java:924-932:
if (credential.getType().equals(UserCredentialModel.KERBEROS)) {
if (kerberosConfig.isAllowKerberosAuthentication()) {
SPNEGOAuthenticator spnegoAuthenticator = (SPNEGOAuthenticator)
credential.getNote(KerberosConstants.AUTHENTICATED_SPNEGO_CONTEXT);
if (spnegoAuthenticator == null) {
String spnegoToken = credential.getChallengeResponse();
spnegoAuthenticator = factory.createSPNEGOAuthenticator(spnegoToken, kerberosConfig);
spnegoAuthenticator.authenticate();
}
// ... process authentication result
}
}
Requirements for SPNEGO Authentication:
- Kerberos realm properly configured
- Server principal (SPN) registered in KDC
- Keytab file accessible to Keycloak
- Browser configured for SPNEGO (trusted sites)
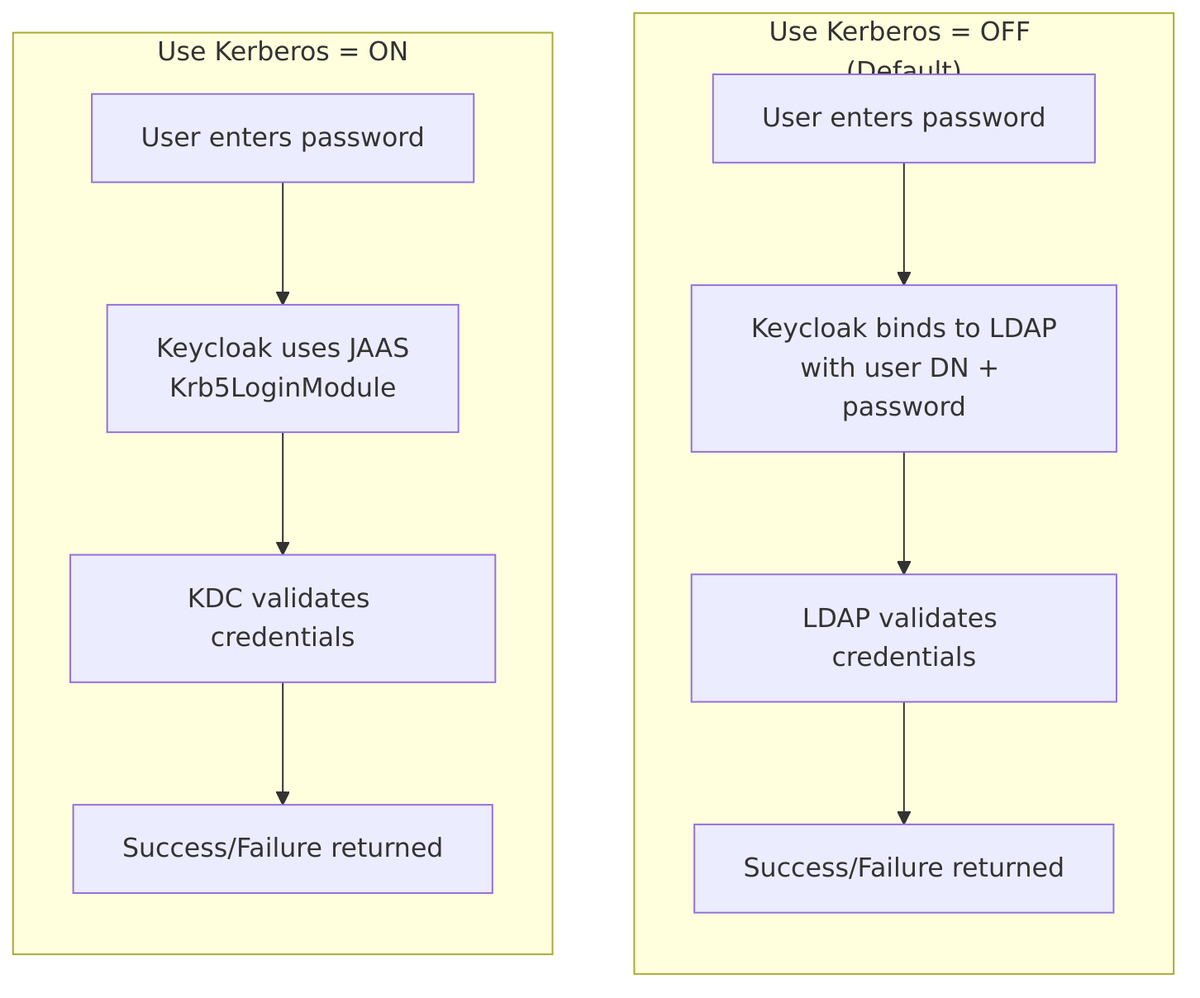
Use Kerberos for Password Authentication
Use Kerberos for Password Authentication controls how password validation is performed when a user enters a password.
Source Code Reference – LDAPProviderKerberosConfig.java:41-43:
public static final String USE_KERBEROS_FOR_PASSWORD_AUTHENTICATION = "useKerberosForPasswordAuthentication";
public boolean isUseKerberosForPasswordAuthentication() {
return Boolean.valueOf(getConfig().getFirst(KerberosConstants.USE_KERBEROS_FOR_PASSWORD_AUTHENTICATION));
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Off (default) | Password validated via LDAP bind operation |
| On | Password validated via Kerberos KDC (JAAS Krb5LoginModule) |
Comparison:
Source Code – Password validation logic – LDAPStorageProvider.java:806-823:
public boolean validPassword(RealmModel realm, UserModel user, String password) {
if (kerberosConfig.isAllowKerberosAuthentication()
&& kerberosConfig.isUseKerberosForPasswordAuthentication()) {
// Use Kerberos JAAS (Krb5LoginModule)
KerberosUsernamePasswordAuthenticator authenticator =
factory.createKerberosUsernamePasswordAuthenticator(kerberosConfig);
String kerberosUsername = user.getFirstAttribute(KerberosConstants.KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL);
// Fallback to username (backwards compatibility)
if (kerberosUsername == null) kerberosUsername = user.getUsername();
return authenticator.validUser(kerberosUsername, password);
} else {
// Use Naming LDAP API (LDAP bind)
LDAPObject ldapUser = loadAndValidateUser(realm, user);
ldapIdentityStore.validatePassword(ldapUser, password);
return true;
}
}
When to Use Each:
| Scenario | Recommended Setting |
|---|---|
| Standard LDAP authentication | Off – LDAP bind is simpler |
| AD with Kerberos-only password policy | On – Some AD configurations require Kerberos |
| Need to validate against KDC | On – Bypass LDAP for password validation |
| LDAP without Kerberos infrastructure | Off – Kerberos not available |
Additional Kerberos Configuration
When Kerberos authentication is enabled, additional settings are required:
| Setting | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Kerberos Realm | Kerberos realm name | EXAMPLE.COM |
| Server Principal | Service Principal Name (SPN) | HTTP/keycloak.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM |
| KeyTab | Path to keytab file | /etc/keycloak/keycloak.keytab |
| Kerberos Principal Attribute | LDAP attribute storing Kerberos principal | userPrincipalName (AD), krbPrincipalName (FreeIPA) |
| Debug | Enable Kerberos debug logging | false |
Source Code Reference – KerberosConstants.java:69-77:
public static final String ALLOW_KERBEROS_AUTHENTICATION = "allowKerberosAuthentication"; public static final String KERBEROS_REALM = "kerberosRealm"; public static final String SERVER_PRINCIPAL = "serverPrincipal"; public static final String KEYTAB = "keyTab"; public static final String DEBUG = "debug"; public static final String KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_ATTRIBUTE = "krbPrincipalAttribute"; // Vendor-specific Kerberos principal attributes public static final String KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE_KRB5_PRINCIPAL_NAME = "krb5PrincipalName"; // ApacheDS public static final String KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE_KRB_PRINCIPAL_NAME = "krbPrincipalName"; // FreeIPA public static final String KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE_USER_PRINCIPAL_NAME = "userPrincipalName"; // AD
Kerberos Principal Attribute
The Kerberos Principal Attribute specifies which LDAP attribute contains the user’s Kerberos principal name. This is used to:
- Map SPNEGO-authenticated users to LDAP entries
- Determine the username for Kerberos password authentication
Source Code – Principal mapping during user import – LDAPStorageProvider.java:681-689:
if (kerberosConfig.isAllowKerberosAuthentication()
&& kerberosConfig.getKerberosPrincipalAttribute() != null) {
String kerberosPrincipal = ldapUser.getAttributeAsString(
kerberosConfig.getKerberosPrincipalAttribute());
if (kerberosPrincipal != null) {
KerberosPrincipal kerberosPrinc = new KerberosPrincipal(kerberosPrincipal);
user.setSingleAttribute(KerberosConstants.KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL, kerberosPrinc.toString());
}
}
Vendor-Specific Values:
| LDAP Vendor | Kerberos Principal Attribute | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | userPrincipalName |
john@EXAMPLE.COM |
| FreeIPA | krbPrincipalName |
john@EXAMPLE.COM |
| ApacheDS | krb5PrincipalName |
john@EXAMPLE.COM |
Kerberos Authentication Flow Summary
Kerberos Configuration Summary
| Setting | Your Config | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Allow Kerberos Authentication | Off |
SPNEGO/SSO authentication disabled |
| Use Kerberos for Password Auth | Off |
Password validation via LDAP bind |
Typical Configurations:
| Scenario | Allow Kerberos | Use Kerberos for Pwd |
|---|---|---|
| Standard LDAP (no Kerberos) | Off | Off |
| AD with SPNEGO SSO | On | Off |
| AD with SPNEGO + Kerberos pwd | On | On |
| FreeIPA with Kerberos | On | On |
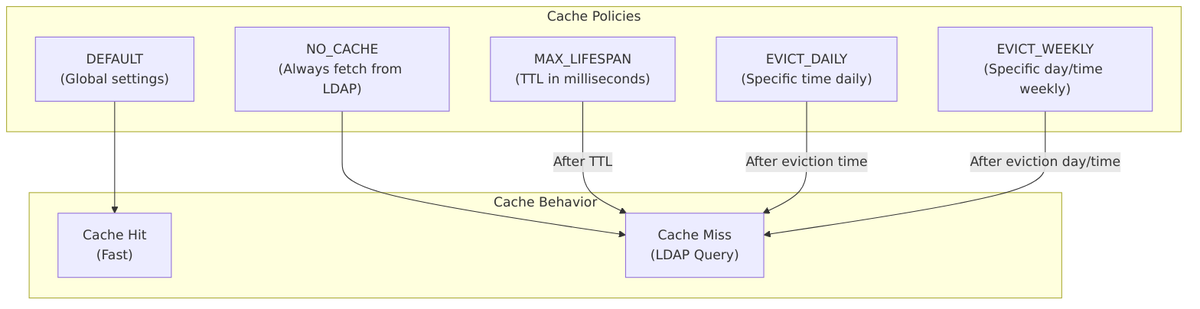
Cache Settings
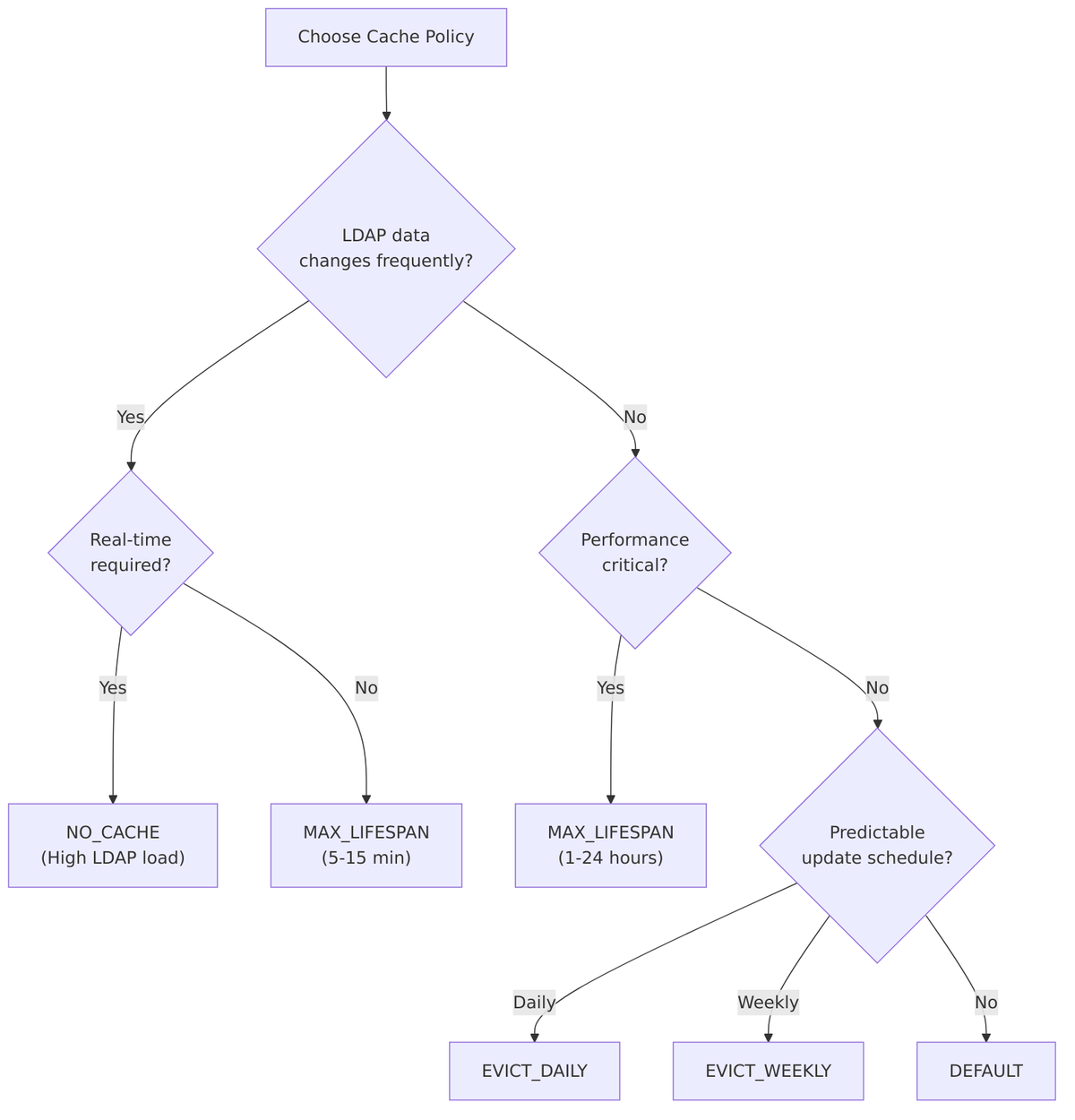
Keycloak caches user data imported from LDAP to improve performance. The Cache Policy controls how long user data remains in the cache before being refreshed from LDAP.
Cache Policy Options
Source Code Reference – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:266-272:
public enum CachePolicy {
NO_CACHE,
DEFAULT,
EVICT_DAILY,
EVICT_WEEKLY,
MAX_LIFESPAN
}
| Policy | Description | Additional Settings |
|---|---|---|
| DEFAULT | Uses global cache settings | None |
| NO_CACHE | Disables caching; always query LDAP | None |
| EVICT_DAILY | Invalidates cache at specific time each day | Eviction Hour, Eviction Minute |
| EVICT_WEEKLY | Invalidates cache on specific day and time | Eviction Day, Eviction Hour, Eviction Minute |
| MAX_LIFESPAN | Cache entries expire after specified TTL | Max Lifespan (milliseconds) |
DEFAULT Policy
Uses whatever cache settings are configured globally for Keycloak. This is the recommended starting point.
Source Code – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:167-168:
if (policy == null || policy == CachePolicy.DEFAULT) {
lifespan = -1; // Use global defaults
}
NO_CACHE Policy
Completely disables caching for this provider. Every user lookup requires an LDAP query.
Source Code – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:191-192:
if (policy == CacheableStorageProviderModel.CachePolicy.NO_CACHE) {
invalidate = true; // Always invalidate = always fetch from LDAP
}
Use Cases:
- Real-time LDAP data requirements
- Debugging/troubleshooting
- Very small user base where LDAP queries are acceptable
Caution: This significantly increases LDAP load and authentication latency.
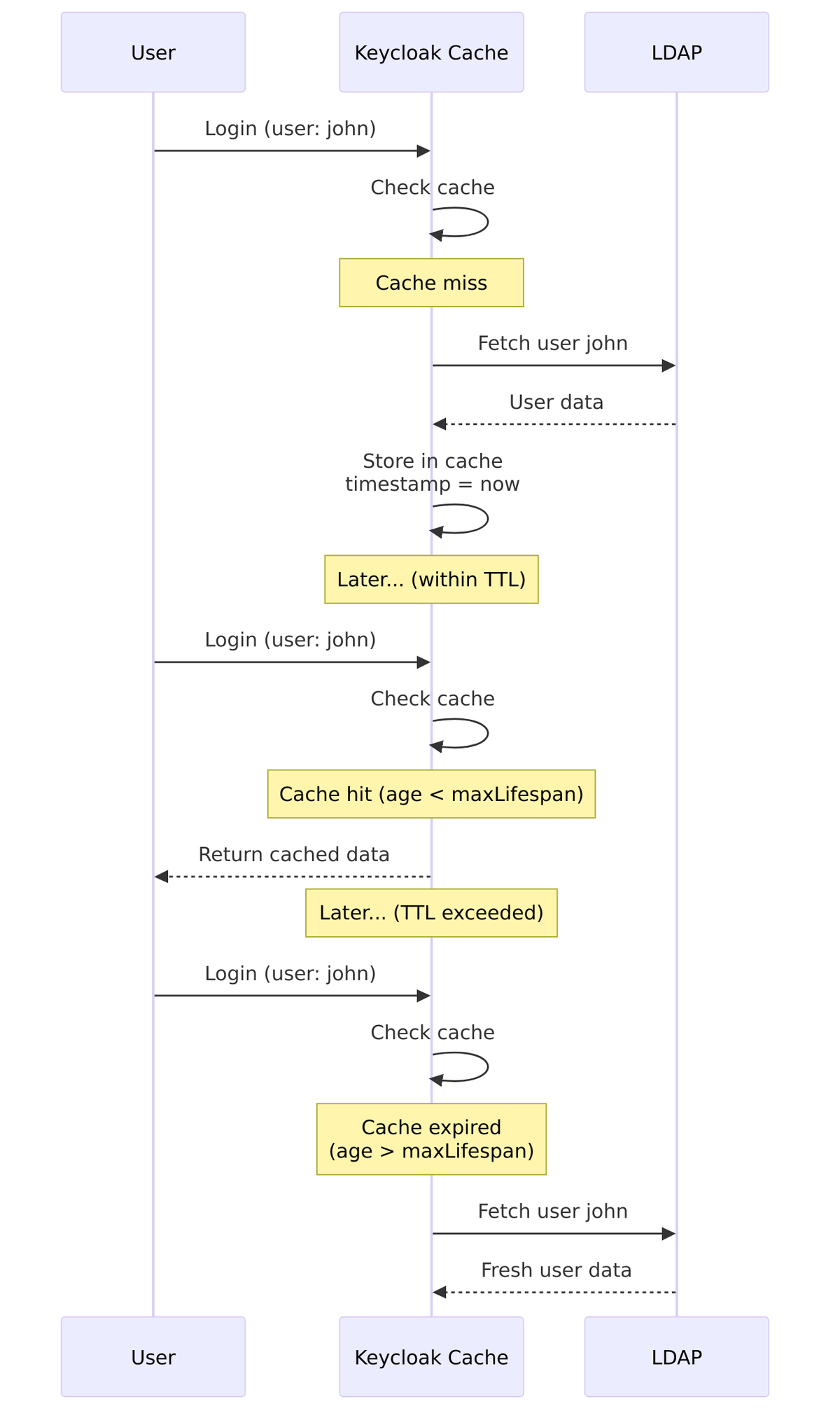
MAX_LIFESPAN Policy
Cache entries are valid for a specified duration (TTL) in milliseconds.
Source Code Reference – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:73-80:
public static final String MAX_LIFESPAN = "maxLifespan";
public long getMaxLifespan() {
if (maxLifespan < 0) {
String str = getConfig().getFirst(MAX_LIFESPAN);
if (str == null) return -1;
maxLifespan = Long.valueOf(str);
}
return maxLifespan;
}
Invalidation Logic – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:195-198:
if (policy == CacheableStorageProviderModel.CachePolicy.MAX_LIFESPAN) {
if (cached.getCacheTimestamp() + getMaxLifespan() < Time.currentTimeMillis()) {
invalidate = true;
}
}
Example Values:
| Value (ms) | Duration |
|---|---|
60000 |
1 minute |
300000 |
5 minutes |
3600000 |
1 hour |
86400000 |
24 hours |
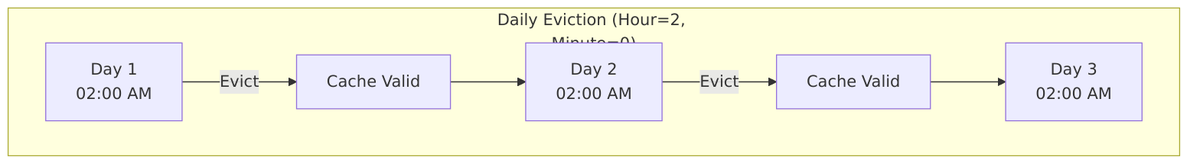
EVICT_DAILY Policy
Cache is invalidated at a specific time every day. All cached users are evicted at this time.
Configuration Properties:
- Eviction Hour (0-23): Hour of day for eviction
- Eviction Minute (0-59): Minute of hour for eviction
Source Code Reference – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:87-100:
public static final String EVICTION_HOUR = "evictionHour";
public static final String EVICTION_MINUTE = "evictionMinute";
public void setEvictionHour(int evictionHour) {
if (evictionHour > 23 || evictionHour < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be between 0 and 23");
this.evictionHour = evictionHour;
getConfig().putSingle(EVICTION_HOUR, Integer.toString(evictionHour));
}
public void setEvictionMinute(int evictionMinute) {
if (evictionMinute > 59 || evictionMinute < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be between 0 and 59");
this.evictionMinute = evictionMinute;
getConfig().putSingle(EVICTION_MINUTE, Integer.toString(evictionMinute));
}
Boundary Calculation – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:233-246:
public static long dailyEvictionBoundary(int hour, int minute) {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.setTimeInMillis(Time.currentTimeMillis());
cal.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, hour);
cal.set(Calendar.MINUTE, minute);
cal.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0);
cal.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND, 0);
if (cal.getTimeInMillis() > Time.currentTimeMillis()) {
// if daily evict for today hasn't happened yet
// set boundary to yesterday's time of eviction
cal.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR, -1);
}
return cal.getTimeInMillis();
}
Example: Eviction Hour = 2, Eviction Minute = 0
- Cache evicted daily at 2:00 AM
- Users cached after 2:00 AM remain valid until next day’s 2:00 AM
EVICT_WEEKLY Policy
Cache is invalidated on a specific day of the week at a specific time.
Configuration Properties:
- Eviction Day (1-7): Day of week (1=Sunday, 2=Monday, …, 7=Saturday)
- Eviction Hour (0-23): Hour of day for eviction
- Eviction Minute (0-59): Minute of hour for eviction
Source Code Reference – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:117-130:
public static final String EVICTION_DAY = "evictionDay";
public void setEvictionDay(int evictionDay) {
if (evictionDay > 7 || evictionDay < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be between 1 and 7");
this.evictionDay = evictionDay;
getConfig().putSingle(EVICTION_DAY, Integer.toString(evictionDay));
}
Weekly Timeout Calculation – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:248-262:
public static long weeklyTimeout(int day, int hour, int minute) {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.setTimeInMillis(Time.currentTimeMillis());
cal.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, hour);
cal.set(Calendar.MINUTE, minute);
cal.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK, day);
cal.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0);
cal.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND, 0);
if (cal.getTimeInMillis() < Time.currentTimeMillis()) {
int oneWeek = (7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000);
cal.add(Calendar.MILLISECOND, oneWeek);
}
return cal.getTimeInMillis();
}
Day of Week Values:
| Value | Day |
|---|---|
| 1 | Sunday |
| 2 | Monday |
| 3 | Tuesday |
| 4 | Wednesday |
| 5 | Thursday |
| 6 | Friday |
| 7 | Saturday |
Example: Eviction Day = 1 (Sunday), Hour = 3, Minute = 0
- Cache evicted every Sunday at 3:00 AM
- Good for weekly LDAP maintenance windows
Cache Invalidation Logic
The shouldInvalidate() method determines if cached data should be refreshed:
Source Code – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:183-217:
public boolean shouldInvalidate(CachedObject cached) {
boolean invalidate = false;
if (!isEnabled()) {
invalidate = true; // Provider disabled = invalidate all
} else {
CachePolicy policy = getCachePolicy();
if (policy != null) {
if (policy == CachePolicy.NO_CACHE) {
invalidate = true;
} else if (cached.getCacheTimestamp() < getCacheInvalidBefore()) {
invalidate = true; // Manual invalidation
} else if (policy == CachePolicy.MAX_LIFESPAN) {
if (cached.getCacheTimestamp() + getMaxLifespan() < Time.currentTimeMillis()) {
invalidate = true;
}
} else if (policy == CachePolicy.EVICT_DAILY) {
long dailyBoundary = dailyEvictionBoundary(getEvictionHour(), getEvictionMinute());
if (cached.getCacheTimestamp() <= dailyBoundary) {
invalidate = true;
}
} else if (policy == CachePolicy.EVICT_WEEKLY) {
int oneWeek = 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000;
long weeklyTimeout = weeklyTimeout(getEvictionDay(), getEvictionHour(), getEvictionMinute());
long lastTimeout = weeklyTimeout - oneWeek;
if (cached.getCacheTimestamp() <= lastTimeout) {
invalidate = true;
}
}
}
}
return invalidate;
}
Manual Cache Invalidation
The cacheInvalidBefore property allows manual invalidation of all cached data before a specific timestamp.
Source Code Reference – CacheableStorageProviderModel.java:132-144:
public static final String CACHE_INVALID_BEFORE = "cacheInvalidBefore";
public long getCacheInvalidBefore() {
if (cacheInvalidBefore < 0) {
String str = getConfig().getFirst(CACHE_INVALID_BEFORE);
if (str == null) return -1;
cacheInvalidBefore = Long.valueOf(str);
}
return cacheInvalidBefore;
}
This is used when you need to force cache refresh (e.g., after LDAP data migration).
Cache Policy Recommendations
| Scenario | Recommended Policy | Settings |
|---|---|---|
| General use | DEFAULT | Use global settings |
| Frequently changing LDAP | MAX_LIFESPAN | 5-15 minutes |
| Stable LDAP, daily updates | EVICT_DAILY | During off-peak hours |
| Stable LDAP, weekly sync | EVICT_WEEKLY | During maintenance window |
| Real-time requirements | NO_CACHE | (High LDAP load) |
| High performance needs | MAX_LIFESPAN | 1-24 hours |
Cache Settings Summary
| Setting | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Cache Policy | How cache entries are invalidated | DEFAULT |
| Max Lifespan | TTL for MAX_LIFESPAN policy (ms) | – |
| Eviction Hour | Hour for EVICT_DAILY/WEEKLY (0-23) | – |
| Eviction Minute | Minute for EVICT_DAILY/WEEKLY (0-59) | – |
| Eviction Day | Day for EVICT_WEEKLY (1=Sun, 7=Sat) | – |
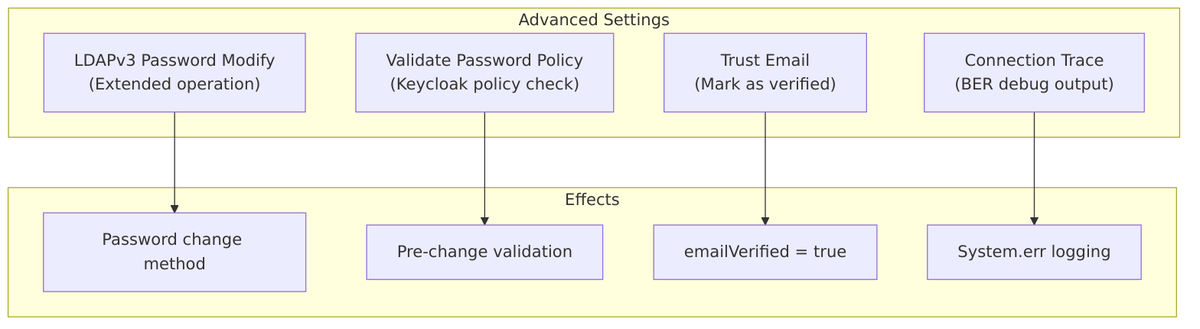
Advanced Settings
These advanced settings control specialized LDAP features for password handling, email verification, and debugging.
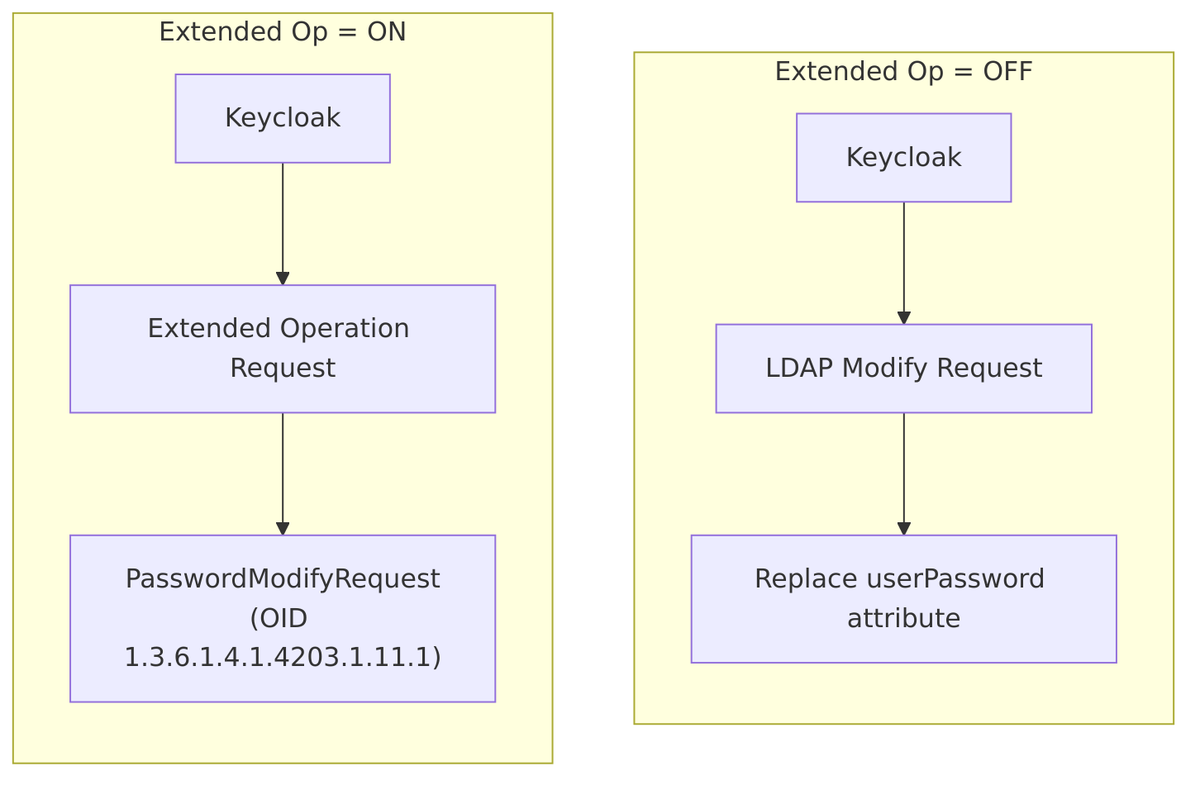
Enable LDAPv3 Password Modify Extended Operation
Controls how password changes are sent to LDAP. When enabled, uses the RFC 3062 Password Modify Extended Operation instead of directly modifying the userPassword attribute.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:65-68:
public static final String USE_PASSWORD_MODIFY_EXTENDED_OP = "usePasswordModifyExtendedOp";
public boolean useExtendedPasswordModifyOp() {
String value = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.USE_PASSWORD_MODIFY_EXTENDED_OP);
return Boolean.parseBoolean(value);
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Off (default) | Modify userPassword attribute directly |
| On | Use Password Modify Extended Operation (RFC 3062) |
Password Update Methods:
Source Code – Password update implementation – LDAPIdentityStore.java:370-376:
if (config.useExtendedPasswordModifyOp()) {
// Use RFC 3062 Password Modify Extended Operation
operationManager.passwordModifyExtended(user.getDn().getLdapName(), password, decorator);
} else {
// Direct attribute modification
ModificationItem[] mods = new ModificationItem[1];
BasicAttribute mod0 = new BasicAttribute(LDAPConstants.USER_PASSWORD_ATTRIBUTE, password);
mods[0] = new ModificationItem(DirContext.REPLACE_ATTRIBUTE, mod0);
operationManager.modifyAttributes(user.getDn().getLdapName(), mods, decorator);
}
Extended Operation Implementation – LDAPOperationManager.java:697-702:
public void passwordModifyExtended(LdapName dn, String password, LDAPOperationDecorator decorator) {
execute(context -> {
PasswordModifyRequest modifyRequest = new PasswordModifyRequest(dn.toString(), null, password);
return context.extendedOperation(modifyRequest);
}, decorator);
}
When to Use:
| Scenario | Recommended |
|---|---|
| OpenLDAP with ppolicy overlay | On – Required for password policy enforcement |
| 389 Directory Server | On – Better password handling |
| Active Directory | Off – AD uses different mechanism |
| LDAP without extended op support | Off – Not supported |
Special Behavior with Sync Registrations:
When both “Sync Registrations” and “Password Modify Extended Op” are enabled, Keycloak creates a hardcoded mapper to set a random initial password:
// LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java:485-491
if (!activeDirectory && syncRegistrations && ldapConfig.useExtendedPasswordModifyOp()) {
// Create mapper to set random "userPassword" on user creation
// Otherwise users won't be able to register and login
mapperModel = KeycloakModelUtils.createComponentModel(
"random initial password",
model.getId(),
HardcodedLDAPAttributeMapperFactory.PROVIDER_ID,
HardcodedLDAPAttributeMapper.LDAP_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, LDAPConstants.USER_PASSWORD_ATTRIBUTE,
HardcodedLDAPAttributeMapper.LDAP_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE, HardcodedLDAPAttributeMapper.RANDOM_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE);
}
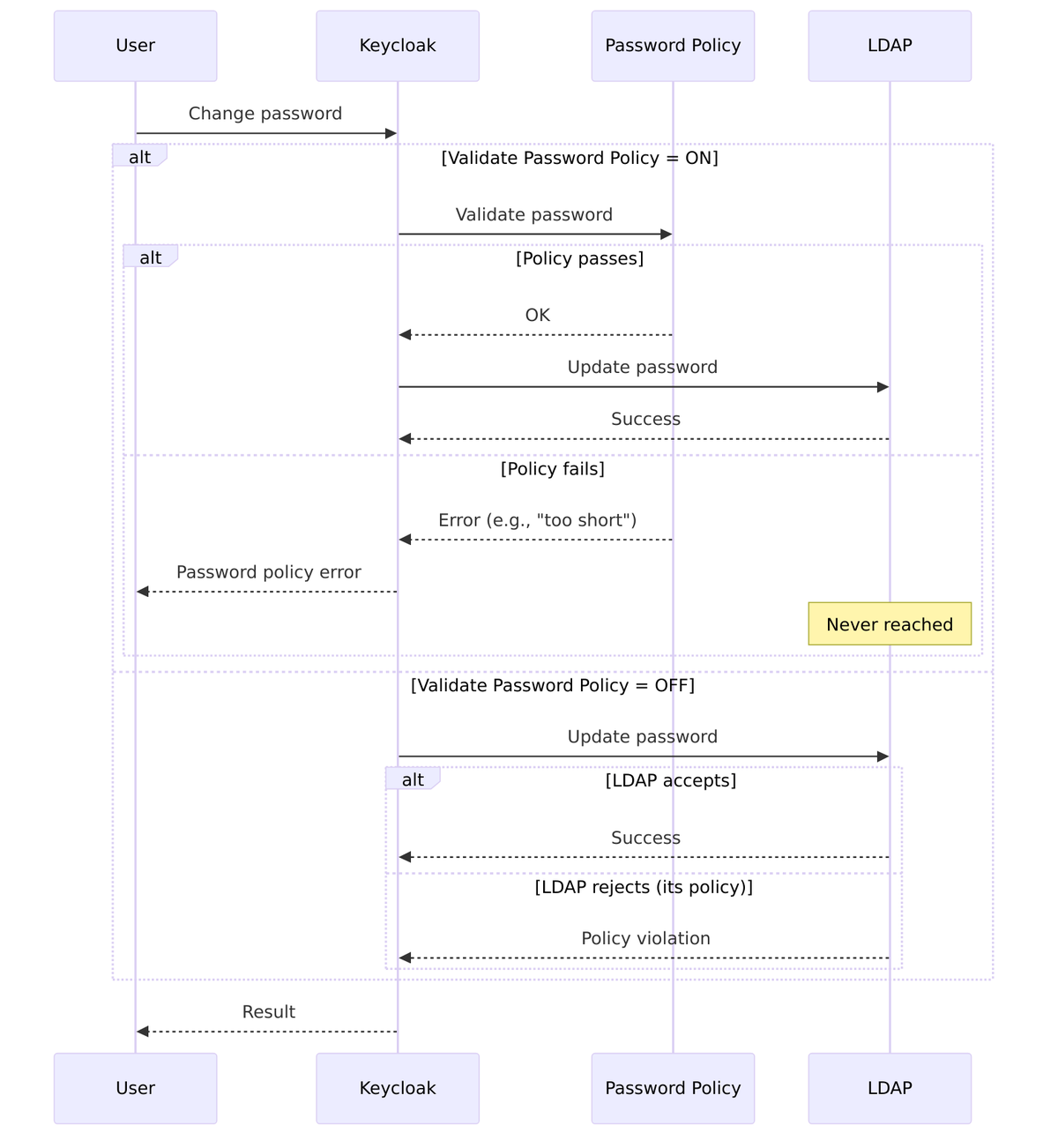
Validate Password Policy
When enabled, Keycloak validates new passwords against its configured password policy before sending the password change to LDAP.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:129-132:
public static final String VALIDATE_PASSWORD_POLICY = "validatePasswordPolicy";
public boolean isValidatePasswordPolicy() {
String validatePPolicy = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.VALIDATE_PASSWORD_POLICY);
return Boolean.parseBoolean(validatePPolicy);
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Off (default) | Password sent directly to LDAP (LDAP enforces its policy) |
| On | Keycloak validates against realm’s password policy first |
Validation Flow:
Source Code – Password validation – LDAPStorageProvider.java:856-859:
if (ldapIdentityStore.getConfig().isValidatePasswordPolicy()) {
PolicyError error = session.getProvider(PasswordPolicyManagerProvider.class)
.validate(realm, user, password);
if (error != null) {
throw new ModelException(error.getMessage(), error.getParameters());
}
}
Requirement: Only available in WRITABLE edit mode.
Source Code – Validation check – LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java:290-294:
// validatePasswordPolicy applicable only for WRITABLE mode
if (cfg.getEditMode() != UserStorageProvider.EditMode.WRITABLE) {
if (cfg.isValidatePasswordPolicy()) {
throw new ComponentValidationException("ldapErrorValidatePasswordPolicyAvailableForWritableOnly");
}
}
Use Cases:
| Scenario | Recommended |
|---|---|
| LDAP has weak/no password policy | On – Use Keycloak’s policy |
| LDAP has strong password policy | Off – Let LDAP enforce |
| Consistent policy across all users | On – Same rules for local and LDAP users |
| Different policies per directory | Off – Let each LDAP enforce its own |
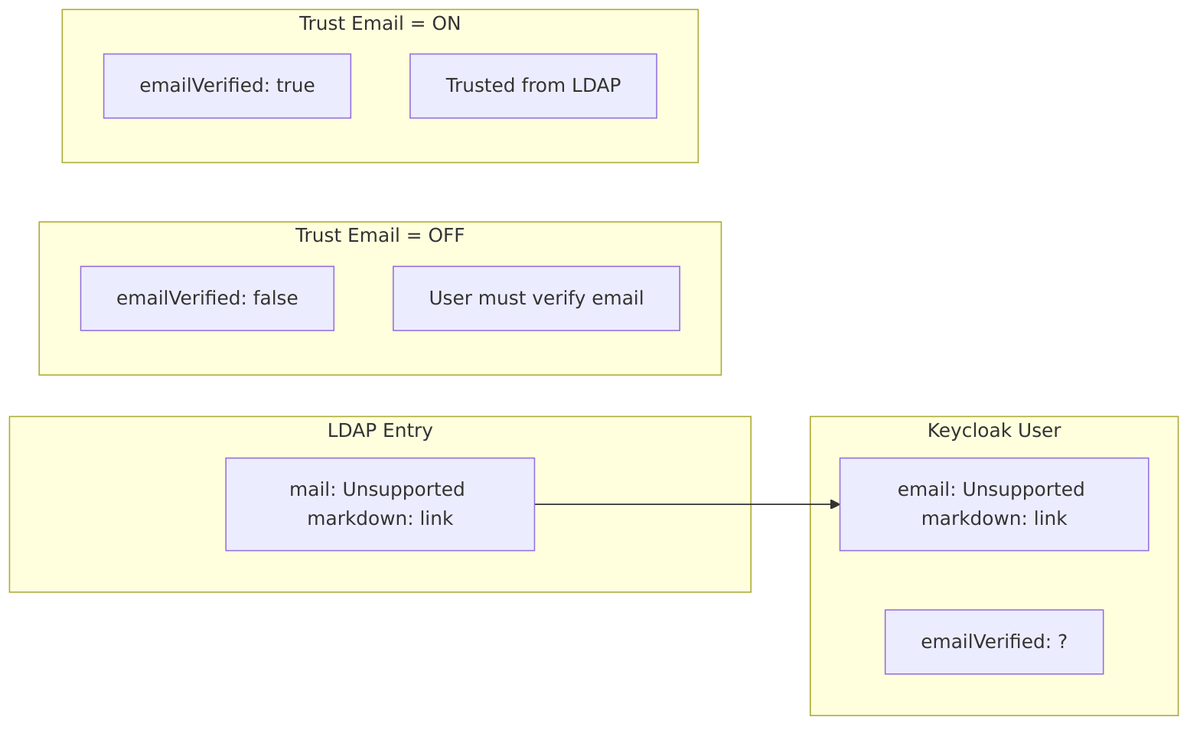
Trust Email
When enabled, email addresses from LDAP are automatically marked as verified in Keycloak.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:134-137:
public static final String TRUST_EMAIL = "trustEmail";
public boolean isTrustEmail() {
String trustEmail = config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.TRUST_EMAIL);
return Boolean.parseBoolean(trustEmail);
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Off (default) | Email not automatically verified |
| On | emailVerified = true when user imported from LDAP |
Source Code – Email verification – LDAPStorageProvider.java:678-680:
if (getLdapIdentityStore().getConfig().isTrustEmail()) {
user.setEmailVerified(true);
}
Effect:
When to Use:
| Scenario | Recommended |
|---|---|
| Corporate LDAP (verified emails) | On – Emails are trusted |
| External/untrusted LDAP | Off – Require verification |
| Email used for password reset | On – Enables reset without verification |
| Compliance requires verification | Off – User must verify |
Connection Trace
Enables detailed BER (Basic Encoding Rules) tracing of LDAP protocol messages for debugging.
Source Code Reference – LDAPConfig.java:269:
public static final String CONNECTION_TRACE = "connectionTrace";
public static final String CONNECTION_TRACE_BER = "com.sun.jndi.ldap.trace.ber";
public boolean isConnectionTrace() {
return Boolean.parseBoolean(config.getFirstOrDefault(
LDAPConstants.CONNECTION_TRACE, Boolean.FALSE.toString()));
}
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Off (default) | No protocol tracing |
| On | BER trace output written to System.err |
Source Code – Trace enabling – LDAPContextManager.java:77-79:
if (ldapConfig.isConnectionTrace()) {
connProp.put(LDAPConstants.CONNECTION_TRACE_BER, System.err);
}
What Gets Logged:
When enabled, you’ll see detailed LDAP protocol messages in stderr:
- Bind requests/responses
- Search requests/responses
- Modify operations
- Extended operations
- All ASN.1/BER encoded data
Example Output:
>>> BER:encode(BIND)
dn: cn=admin,dc=example,dc=com
version: 3
<<< BER:decode(BIND_RESPONSE)
resultCode: success
>>> BER:encode(SEARCH)
base: ou=People,dc=example,dc=com
filter: (uid=john)
...
When to Use:
| Scenario | Recommended |
|---|---|
| Production | Off – Performance impact, verbose logging |
| Debugging LDAP issues | On – See actual protocol messages |
| Troubleshooting authentication | On – Verify what’s sent/received |
| Development/testing | On (as needed) |
Caution: Connection tracing can expose sensitive data (including passwords in some operations) in logs. Only enable temporarily for debugging.
Advanced Settings Summary
| Setting | Your Config | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LDAPv3 Password Modify Extended Op | Off |
Use attribute modification (not RFC 3062) |
| Validate Password Policy | Off |
Let LDAP enforce password policy |
| Trust Email | Off |
Email addresses not automatically verified |
| Connection Trace | Off |
No BER protocol tracing |
Typical Configurations:
| LDAP Type | Password Modify | Validate Policy | Trust Email |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | Off | Off | On |
| OpenLDAP with ppolicy | On | Off | On |
| 389 Directory | On | Off | On |
| Untrusted external LDAP | Off | On | Off |
LDAP Mappers
Mapper Interface
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/mappers/LDAPStorageMapper.java
public interface LDAPStorageMapper extends Provider {
// Sync data from LDAP to Keycloak (e.g., during full sync)
void syncDataFromFederationProviderToKeycloak(RealmModel realm);
// Sync data from Keycloak to LDAP (e.g., during user update)
void syncDataFromKeycloakToFederationProvider(RealmModel realm);
// Called when user is imported from LDAP
void onImportUserFromLDAP(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel user,
RealmModel realm, boolean isCreate);
// Called when user is registered in Keycloak and needs to be created in LDAP
void onRegisterUserToLDAP(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel localUser,
RealmModel realm);
// Wrap user model with mapper-specific behavior
UserModel proxy(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel delegate,
RealmModel realm);
// Modify LDAP query before execution
void beforeLDAPQuery(LDAPQuery query);
// Handle authentication failures
boolean onAuthenticationFailure(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel user,
AuthenticationException exception,
RealmModel realm);
}
User Attribute Mapper
Maps LDAP attributes to Keycloak user attributes:
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/mappers/UserAttributeLDAPStorageMapper.java
public class UserAttributeLDAPStorageMapper extends AbstractLDAPStorageMapper {
public static final String USER_MODEL_ATTRIBUTE = "user.model.attribute";
public static final String LDAP_ATTRIBUTE = "ldap.attribute";
public static final String READ_ONLY = "read.only";
public static final String ALWAYS_READ_VALUE_FROM_LDAP = "always.read.value.from.ldap";
public static final String IS_MANDATORY_IN_LDAP = "is.mandatory.in.ldap";
public static final String IS_BINARY_ATTRIBUTE = "is.binary.attribute";
public static final String ATTRIBUTE_DEFAULT_VALUE = "attribute.default.value";
@Override
public void onImportUserFromLDAP(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel user,
RealmModel realm, boolean isCreate) {
String userModelAttr = mapperModel.get(USER_MODEL_ATTRIBUTE);
String ldapAttr = mapperModel.get(LDAP_ATTRIBUTE);
// Get value from LDAP
Object ldapValue = ldapUser.getAttributeAsSet(ldapAttr);
// Map to Keycloak user attribute
if (ldapValue != null) {
if (isBinaryAttribute()) {
// Handle binary (e.g., certificate)
user.setSingleAttribute(userModelAttr, Base64.encode(ldapValue));
} else {
user.setSingleAttribute(userModelAttr, ldapValue.toString());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onRegisterUserToLDAP(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel localUser,
RealmModel realm) {
String userModelAttr = mapperModel.get(USER_MODEL_ATTRIBUTE);
String ldapAttr = mapperModel.get(LDAP_ATTRIBUTE);
// Get value from Keycloak user
String value = localUser.getFirstAttribute(userModelAttr);
// Set in LDAP object
if (value != null) {
ldapUser.setSingleAttribute(ldapAttr, value);
} else if (isMandatory()) {
// Use default value for mandatory attributes
String defaultValue = mapperModel.get(ATTRIBUTE_DEFAULT_VALUE);
ldapUser.setSingleAttribute(ldapAttr, defaultValue);
}
}
}
Group Mapper
Synchronizes LDAP groups with Keycloak groups:
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/mappers/membership/group/GroupLDAPStorageMapper.java
public class GroupLDAPStorageMapper extends AbstractLDAPStorageMapper
implements LDAPStorageMapper {
// Configuration properties
public static final String GROUPS_DN = "groups.dn";
public static final String GROUP_NAME_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE = "group.name.ldap.attribute";
public static final String GROUP_OBJECT_CLASSES = "group.object.classes";
public static final String MEMBERSHIP_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE = "membership.ldap.attribute";
public static final String MEMBERSHIP_ATTRIBUTE_TYPE = "membership.attribute.type";
public static final String GROUPS_LDAP_FILTER = "groups.ldap.filter";
public static final String MODE = "mode";
public static final String USER_ROLES_RETRIEVE_STRATEGY = "user.roles.retrieve.strategy";
public static final String MAPPED_GROUP_ATTRIBUTES = "mapped.group.attributes";
@Override
public void syncDataFromFederationProviderToKeycloak(RealmModel realm) {
// Query all LDAP groups
try (LDAPQuery ldapQuery = createGroupQuery(false)) {
List<ldapobject> ldapGroups = ldapQuery.getResultList();
// Import each group to Keycloak
for (LDAPObject ldapGroup : ldapGroups) {
String groupName = getGroupName(ldapGroup);
GroupModel kcGroup = realm.getGroupsStream()
.filter(g -> g.getName().equals(groupName))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
if (kcGroup == null) {
// Create new group
kcGroup = realm.createGroup(groupName);
}
// Sync group attributes
syncGroupAttributes(ldapGroup, kcGroup);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onImportUserFromLDAP(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel user,
RealmModel realm, boolean isCreate) {
// Get user's group memberships from LDAP
Set<ldapobject> ldapGroups = getLDAPGroupsOfUser(ldapUser);
for (LDAPObject ldapGroup : ldapGroups) {
String groupName = getGroupName(ldapGroup);
GroupModel kcGroup = KeycloakModelUtils.findGroupByPath(realm, "/" + groupName);
if (kcGroup != null) {
user.joinGroup(kcGroup);
}
}
}
// Membership types
public enum MembershipType {
DN, // Member attribute contains full DN
UID, // Member attribute contains UID
EMAIL // Member attribute contains email
}
// Mapper modes
public enum Mode {
LDAP_ONLY, // Groups exist only in LDAP
IMPORT, // Import groups to Keycloak
READ_ONLY // Read-only sync
}
}
Role Mapper
Maps LDAP groups to Keycloak roles:
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/mappers/membership/role/RoleLDAPStorageMapper.java
public class RoleLDAPStorageMapper extends AbstractLDAPStorageMapper {
public static final String ROLES_DN = "roles.dn";
public static final String ROLE_NAME_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE = "role.name.ldap.attribute";
public static final String ROLE_OBJECT_CLASSES = "role.object.classes";
public static final String MEMBERSHIP_LDAP_ATTRIBUTE = "membership.ldap.attribute";
public static final String USE_REALM_ROLES_MAPPING = "use.realm.roles.mapping";
public static final String CLIENT_ID = "client.id";
@Override
public void onImportUserFromLDAP(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel user,
RealmModel realm, boolean isCreate) {
// Get user's role memberships from LDAP
Set<ldapobject> ldapRoles = getLDAPRolesOfUser(ldapUser);
for (LDAPObject ldapRole : ldapRoles) {
String roleName = getRoleName(ldapRole);
RoleModel role;
if (useRealmRoles()) {
role = realm.getRole(roleName);
} else {
ClientModel client = realm.getClientByClientId(getClientId());
role = client.getRole(roleName);
}
if (role != null) {
user.grantRole(role);
}
}
}
}
MS Active Directory Account Control Mapper
Handles AD-specific user account flags:
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/mappers/msad/MSADUserAccountControlStorageMapper.java
public class MSADUserAccountControlStorageMapper extends AbstractLDAPStorageMapper
implements PasswordUpdateCallback {
// AD userAccountControl flags
public static final int ACCOUNT_DISABLED = 0x0002;
public static final int LOCKOUT = 0x0010;
public static final int PASSWORD_EXPIRED = 0x800000;
public static final int NORMAL_ACCOUNT = 0x0200;
public static final int DONT_EXPIRE_PASSWORD = 0x10000;
@Override
public void onImportUserFromLDAP(LDAPObject ldapUser, UserModel user,
RealmModel realm, boolean isCreate) {
String uacValue = ldapUser.getAttributeAsString("userAccountControl");
if (uacValue != null) {
int uac = Integer.parseInt(uacValue);
// Check if account is disabled
boolean disabled = (uac & ACCOUNT_DISABLED) != 0;
user.setEnabled(!disabled);
// Check if account is locked
boolean locked = (uac & LOCKOUT) != 0;
if (locked) {
// Handle lockout
}
}
}
@Override
public void passwordUpdated(UserModel user, LDAPObject ldapUser,
CredentialInput input) {
// Clear password-related flags after successful password update
String uacValue = ldapUser.getAttributeAsString("userAccountControl");
int uac = Integer.parseInt(uacValue);
// Remove LOCKOUT and PASSWORD_EXPIRED flags
uac &= ~LOCKOUT;
uac &= ~PASSWORD_EXPIRED;
ldapUser.setSingleAttribute("userAccountControl", String.valueOf(uac));
}
}
Authentication
Password Validation
Password validation is done via LDAP bind:
// LDAPStorageProvider.java
@Override
public boolean isValid(RealmModel realm, UserModel user, CredentialInput input) {
if (!supportsCredentialType(input.getType())) {
return false;
}
// Get LDAP user object
LDAPObject ldapUser = loadAndValidateUser(realm, user);
if (ldapUser == null) {
return false;
}
String password = input.getChallengeResponse();
try {
// Attempt Kerberos authentication first (if configured)
if (kerberosConfig.isEnabled()) {
boolean kerberosAuth = validKerberosPassword(ldapUser, password);
if (kerberosAuth) {
return true;
}
}
// Fall back to LDAP bind authentication
return ldapIdentityStore.validatePassword(ldapUser, password);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
// Handle authentication failure through mappers
boolean handled = handleAuthenticationFailure(ldapUser, user, e, realm);
return false;
}
}
// LDAPIdentityStore.java
public boolean validatePassword(LDAPObject user, String password) {
String userDn = user.getDn().toString();
try {
// Create new LDAP context with user credentials
LDAPContextManager ldapContextManager = LDAPContextManager.builder()
.setConfig(config)
.setBindDn(userDn)
.setBindCredential(password)
.build();
// Attempt bind - throws AuthenticationException if invalid
ldapContextManager.getLdapContext();
return true;
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
return false;
}
}
Password Updates
Password updates (WRITABLE mode only):
// LDAPStorageProvider.java
@Override
public boolean updateCredential(RealmModel realm, UserModel user,
CredentialInput input) {
if (!supportsCredentialType(input.getType())) {
return false;
}
if (editMode == EditMode.READ_ONLY) {
throw new ReadOnlyException("Cannot update password in read-only mode");
}
LDAPObject ldapUser = loadAndValidateUser(realm, user);
String password = input.getChallengeResponse();
// Optional: Validate against Keycloak password policy
if (config.isValidatePasswordPolicy()) {
PolicyError error = session.getProvider(PasswordPolicyManagerProvider.class)
.validate(realm, user, password);
if (error != null) {
throw new ModelException(error.getMessage());
}
}
// Call mapper callbacks before password update
LDAPOperationDecorator decorator = getOperationDecorator(ldapUser, user, input);
try {
// Update password in LDAP
ldapIdentityStore.updatePassword(ldapUser, password, decorator);
// Call mapper callbacks after success
getPasswordUpdateCallbacks().forEach(cb ->
cb.passwordUpdated(user, ldapUser, input));
return true;
} catch (ModelException e) {
// Call mapper callbacks on failure
getPasswordUpdateCallbacks().forEach(cb ->
cb.passwordUpdateFailed(user, ldapUser, input, e));
throw e;
}
}
Kerberos/SPNEGO Authentication
// LDAPStorageProvider.java
@Override
public CredentialValidationOutput authenticate(RealmModel realm,
CredentialInput input) {
if (!(input instanceof UserCredentialModel)) {
return null;
}
if (kerberosConfig.isEnabled() &&
input.getType().equals(KerberosConstants.KERBEROS_AUTHENTICATION)) {
// SPNEGO token authentication
String spnegoToken = input.getChallengeResponse();
SPNEGOAuthenticator authenticator = factory.createSPNEGOAuthenticator(
spnegoToken, kerberosConfig);
authenticator.authenticate();
if (authenticator.isAuthenticated()) {
// Find or create user based on Kerberos principal
String kerberosUserName = authenticator.getAuthenticatedUsername();
UserModel user = findOrCreateKerberosUser(realm, kerberosUserName);
return new CredentialValidationOutput(user, State.AUTHENTICATED,
authenticator.getDelegationCredential());
}
}
return null;
}
Connection Management
LDAP Context Manager
// federation/ldap/src/main/java/org/keycloak/storage/ldap/idm/store/ldap/LDAPContextManager.java
public class LDAPContextManager implements AutoCloseable {
private final LDAPConfig ldapConfig;
private final KeycloakSession session;
private LdapContext ldapContext;
private StartTlsResponse tlsResponse;
public LdapContext getLdapContext() throws NamingException {
if (ldapContext == null) {
ldapContext = createLdapContext();
}
return ldapContext;
}
private LdapContext createLdapContext() throws NamingException {
Hashtable<object, object=""> env = new Hashtable<>();
env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, ldapConfig.getFactoryName());
env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, ldapConfig.getConnectionUrl());
env.put(Context.SECURITY_AUTHENTICATION, ldapConfig.getAuthType());
// Connection pooling (disabled for StartTLS)
String connectionPooling = ldapConfig.getConnectionPooling();
if (connectionPooling != null) {
env.put("com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool", connectionPooling);
}
// Timeouts
String connectionTimeout = ldapConfig.getConnectionTimeout();
if (connectionTimeout != null) {
env.put("com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.timeout", connectionTimeout);
}
String readTimeout = ldapConfig.getReadTimeout();
if (readTimeout != null) {
env.put("com.sun.jndi.ldap.read.timeout", readTimeout);
}
// Bind credentials (from vault or direct)
String bindDn = ldapConfig.getBindDN();
String bindCredential = getBindCredential();
if (bindDn != null) {
env.put(Context.SECURITY_PRINCIPAL, bindDn);
env.put(Context.SECURITY_CREDENTIALS, bindCredential);
}
LdapContext ctx = new InitialLdapContext(env, null);
// StartTLS if configured
if (ldapConfig.isStartTls()) {
tlsResponse = (StartTlsResponse) ctx.extendedOperation(
new StartTlsRequest());
tlsResponse.negotiate();
}
return ctx;
}
@Override
public void close() {
if (tlsResponse != null) {
try {
tlsResponse.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.warn("Error closing TLS", e);
}
}
if (ldapContext != null) {
try {
ldapContext.close();
} catch (NamingException e) {
logger.warn("Error closing LDAP context", e);
}
}
}
}
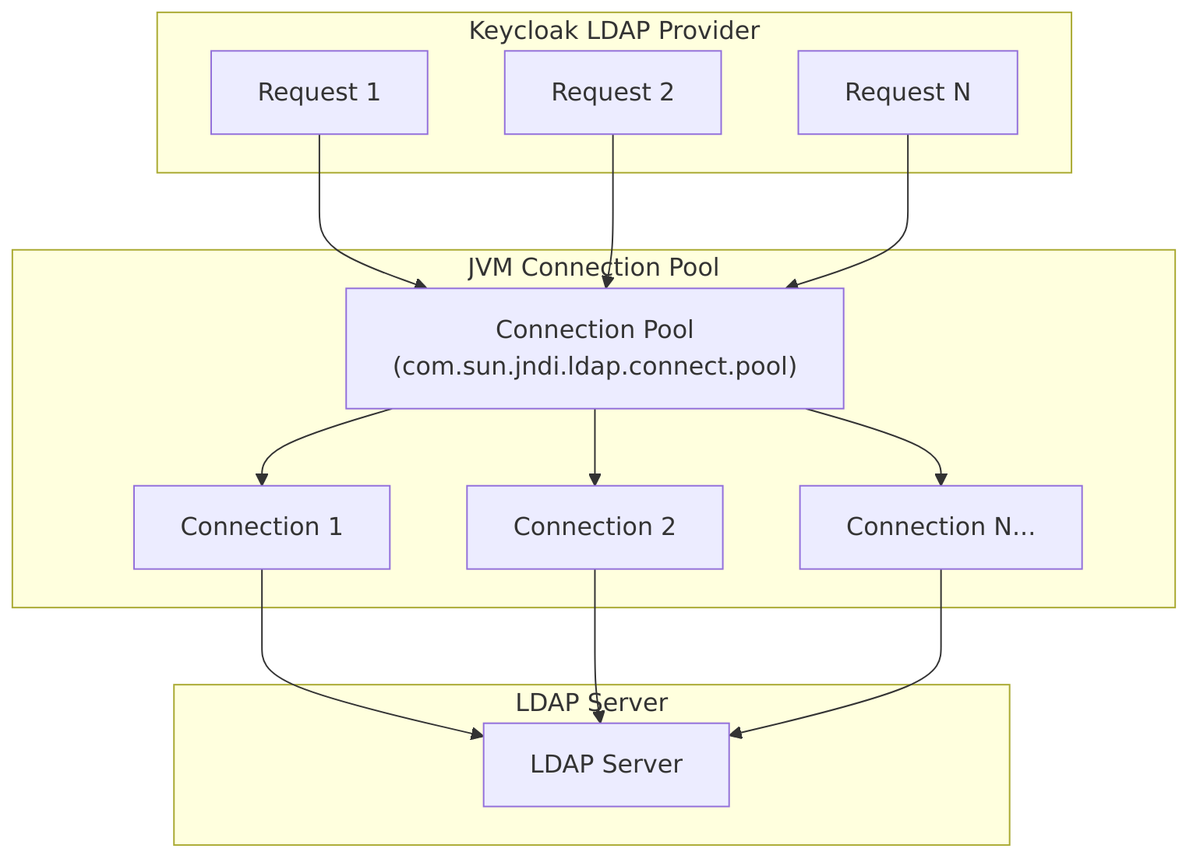
Connection Pooling
LDAP connection pooling in Keycloak uses JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface) built-in connection pooling, managed at the JVM level through system properties.
Pool Protocol Initialization
When Keycloak starts, the LDAPStorageProviderFactory initializes the JVM pool protocol:
// LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java:308-318
@Override
public void init(Config.Scope config) {
// Enable connection pooling for both plain (ldap://) and SSL (ldaps://) protocols
if (System.getProperty("com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.protocol") == null) {
System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.protocol", "plain ssl");
}
}
This sets the JVM system property to enable pooling for:
plain– unencrypted LDAP connections (ldap://)ssl– SSL/TLS encrypted connections (ldaps://)
Per-Connection Pool Setting
Each LDAP connection is configured with pooling enabled/disabled:
// LDAPContextManager.java:205-208
String connectionPooling = ldapConfig.getConnectionPooling();
if (connectionPooling != null) {
env.put("com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool", connectionPooling);
}
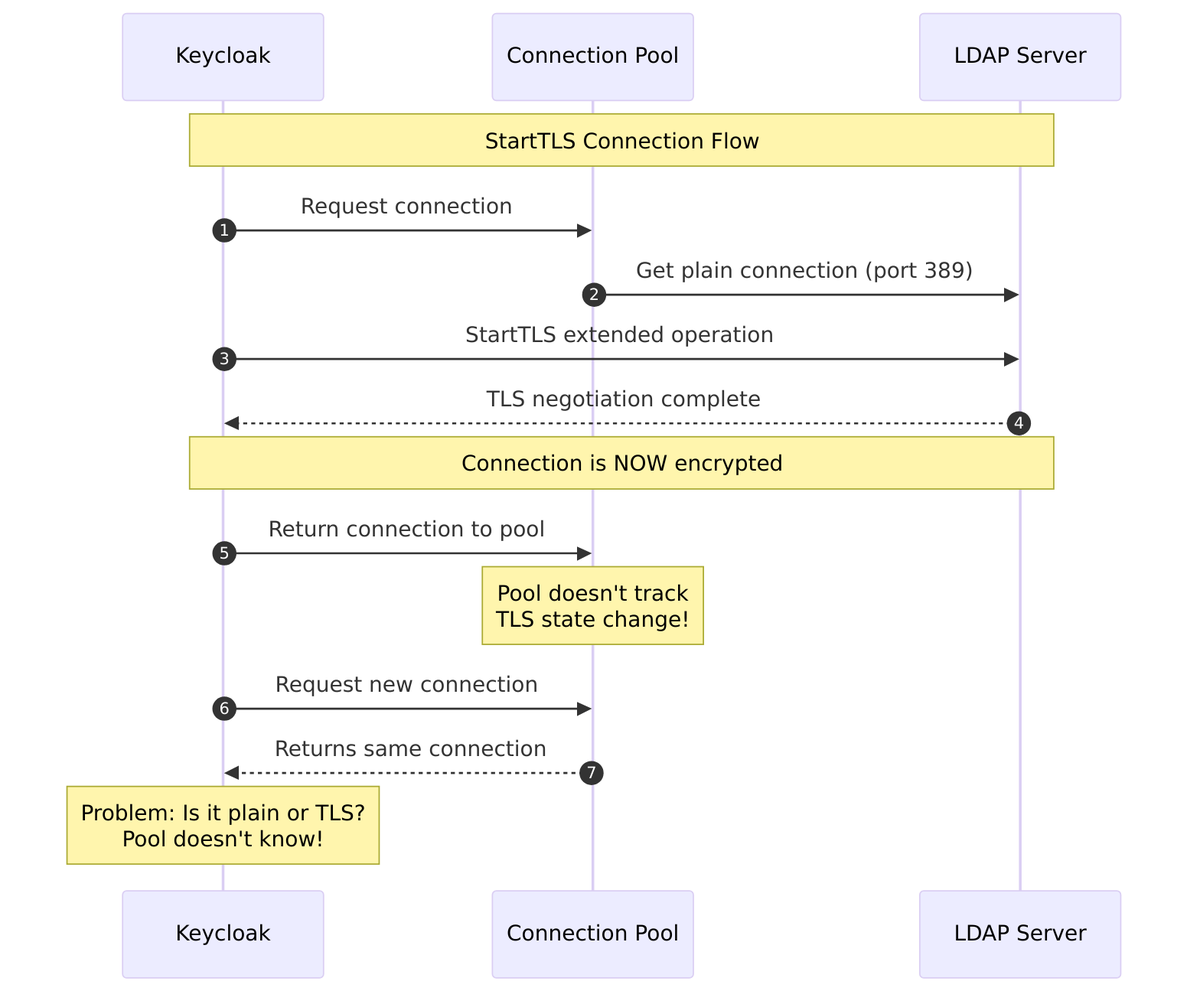
StartTLS and Connection Pooling – Why They’re Incompatible
Connection pooling cannot be used with StartTLS because of how StartTLS works:
The Problem:
- StartTLS begins as a plain LDAP connection on port 389
- After connection is established, the client sends a StartTLS extended operation
- The connection upgrades to TLS encryption
- The connection pool has no knowledge of this state change
- Pooled connections could have inconsistent encryption states
Source Code Enforcement:
// LDAPConfig.java:139-144
public String getConnectionPooling() {
if (isStartTls()) {
return null; // Automatically disable pooling when StartTLS is enabled
} else {
return config.getFirst(LDAPConstants.CONNECTION_POOLING);
}
}
// LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java:280-283 - Validation at configuration time
if (cfg.isStartTls() && Boolean.parseBoolean(
config.getConfig().getFirst(LDAPConstants.CONNECTION_POOLING))) {
throw new ComponentValidationException("ldapErrorCantEnableStartTlsAndConnectionPooling");
}
Password Validation – Always Disables Pooling
Password validation always disables connection pooling to prevent credential caching:
// LDAPOperationManager.java:497-498
// Never use connection pool to prevent password caching
env.put("com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool", "false");
This prevents:
- Caching incorrect passwords as valid
- Credential leakage between users
JNDI Pool System Properties
The JVM provides system properties to configure the pool:
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.protocol |
Protocols to pool (plain, ssl) |
plain |
com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.authentication |
Auth types to pool (none, simple, DIGEST-MD5) |
simple |
com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.maxsize |
Max connections per identity | 0 (unlimited) |
com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.prefsize |
Preferred pool size | 0 |
com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.timeout |
Idle connection timeout (ms) | 0 (no timeout) |
com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.initsize |
Initial pool size | 1 |
com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool.debug |
Enable debug output | false |
Connection Pooling Summary
| Scenario | Connection Pooling | Reason |
|---|---|---|
ldap:// (plain) |
? Enabled | No encryption state to manage |
ldaps:// (SSL) |
? Enabled | SSL established at connect time |
ldap:// + StartTLS |
? Disabled | TLS state changes after connect |
| Password validation | ? Always disabled | Prevent credential caching |
Practical Usage Examples
1. Basic LDAP Configuration (Admin Console)
Provider: ldap Edit Mode: READ_ONLY Vendor: Active Directory Connection URL: ldap://ad.example.com:389 Bind DN: cn=admin,cn=users,dc=example,dc=com Bind Credential: ******** Users DN: cn=users,dc=example,dc=com Username LDAP attribute: sAMAccountName RDN LDAP attribute: cn UUID LDAP attribute: objectGUID User Object Classes: person, organizationalPerson, user Search Scope: Subtree Pagination: On Batch Size For Sync: 1000
2. REST API Configuration
# Get admin token
TOKEN=$(curl -s -X POST \
"http://localhost:8080/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token" \
-d "grant_type=password&client_id=admin-cli&username=admin&password=admin" \
| jq -r '.access_token')
# Create LDAP federation provider
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/admin/realms/myrealm/components" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "ldap",
"providerId": "ldap",
"providerType": "org.keycloak.storage.UserStorageProvider",
"config": {
"editMode": ["READ_ONLY"],
"vendor": ["ad"],
"connectionUrl": ["ldap://ad.example.com:389"],
"bindDn": ["cn=admin,cn=users,dc=example,dc=com"],
"bindCredential": ["secret"],
"usersDn": ["cn=users,dc=example,dc=com"],
"usernameLDAPAttribute": ["sAMAccountName"],
"rdnLDAPAttribute": ["cn"],
"uuidLDAPAttribute": ["objectGUID"],
"userObjectClasses": ["person, organizationalPerson, user"],
"searchScope": ["2"],
"pagination": ["true"],
"batchSizeForSync": ["1000"],
"importEnabled": ["true"],
"syncRegistrations": ["false"]
}
}'
3. Add User Attribute Mapper
LDAP_ID="ldap-provider-id"
# Map department attribute
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/admin/realms/myrealm/components" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"name\": \"department\",
\"providerId\": \"user-attribute-ldap-mapper\",
\"providerType\": \"org.keycloak.storage.ldap.mappers.LDAPStorageMapper\",
\"parentId\": \"$LDAP_ID\",
\"config\": {
\"ldap.attribute\": [\"department\"],
\"user.model.attribute\": [\"department\"],
\"read.only\": [\"true\"],
\"always.read.value.from.ldap\": [\"false\"],
\"is.mandatory.in.ldap\": [\"false\"]
}
}"
4. Add Group Mapper
# Map LDAP groups to Keycloak groups
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/admin/realms/myrealm/components" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"name\": \"ldap-groups\",
\"providerId\": \"group-ldap-mapper\",
\"providerType\": \"org.keycloak.storage.ldap.mappers.LDAPStorageMapper\",
\"parentId\": \"$LDAP_ID\",
\"config\": {
\"groups.dn\": [\"cn=groups,dc=example,dc=com\"],
\"group.name.ldap.attribute\": [\"cn\"],
\"group.object.classes\": [\"groupOfNames\"],
\"membership.ldap.attribute\": [\"member\"],
\"membership.attribute.type\": [\"DN\"],
\"mode\": [\"READ_ONLY\"],
\"user.roles.retrieve.strategy\": [\"LOAD_GROUPS_BY_MEMBER_ATTRIBUTE\"],
\"drop.non.existing.groups.during.sync\": [\"false\"]
}
}"
5. Trigger User Sync
# Full sync curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/admin/realms/myrealm/user-storage/$LDAP_ID/sync?action=triggerFullSync" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" # Changed users sync curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/admin/realms/myrealm/user-storage/$LDAP_ID/sync?action=triggerChangedUsersSync" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
6. Test LDAP Connection
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/admin/realms/myrealm/testLDAPConnection" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"action": "testConnection",
"connectionUrl": "ldap://ad.example.com:389",
"bindDn": "cn=admin,cn=users,dc=example,dc=com",
"bindCredential": "secret",
"useTruststoreSpi": "ldapsOnly",
"connectionTimeout": "5000"
}'
# Test authentication
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/admin/realms/myrealm/testLDAPConnection" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"action": "testAuthentication",
"connectionUrl": "ldap://ad.example.com:389",
"bindDn": "cn=admin,cn=users,dc=example,dc=com",
"bindCredential": "secret",
"useTruststoreSpi": "ldapsOnly"
}'
Vendor-Specific Configuration
Active Directory
"vendor": ["ad"],
"usernameLDAPAttribute": ["sAMAccountName"],
"rdnLDAPAttribute": ["cn"],
"uuidLDAPAttribute": ["objectGUID"],
"userObjectClasses": ["person, organizationalPerson, user"],
"customUserSearchFilter": ["(&(objectClass=user)(!(objectClass=computer)))"]
}
Default Mappers for AD:
- Username mapper (sAMAccountName)
- First/Last name mappers
- Email mapper
- MSAD User Account Control mapper (handles enabled/disabled status)
OpenLDAP
"vendor": ["other"],
"usernameLDAPAttribute": ["uid"],
"rdnLDAPAttribute": ["uid"],
"uuidLDAPAttribute": ["entryUUID"],
"userObjectClasses": ["inetOrgPerson, organizationalPerson"]
}
Red Hat Directory Server
"vendor": ["rhds"],
"usernameLDAPAttribute": ["uid"],
"rdnLDAPAttribute": ["uid"],
"uuidLDAPAttribute": ["nsuniqueid"],
"userObjectClasses": ["inetOrgPerson, organizationalPerson"]
}
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Connection timeout | Firewall or network issue | Check connectivity, increase timeout |
| Invalid credentials | Wrong bind DN or password | Verify bind credentials |
| No users found | Wrong users DN or search scope | Check users DN and search scope |
| Users not importing | Import disabled or edit mode issue | Enable import, check edit mode |
| Password validation fails | LDAP bind restrictions | Check LDAP ACLs for bind |
| Groups not syncing | Missing group mapper | Add group mapper |
| StartTLS fails | Certificate issue | Configure truststore SPI |
Debug Logging
Enable LDAP debug logging in Keycloak:
# Start Keycloak with debug logging bin/kc.sh start-dev --log-level=org.keycloak.storage.ldap:debug
Or in standalone configuration:
<logger category="org.keycloak.storage.ldap"> <level name="DEBUG"></level> </logger>
Connection Testing
// Test connection programmatically
LDAPContextManager manager = LDAPContextManager.builder()
.setConfig(ldapConfig)
.build();
try {
LdapContext ctx = manager.getLdapContext();
// Connection successful
Attributes attrs = ctx.getAttributes("");
// Check root DSE
} catch (NamingException e) {
// Connection failed
logger.error("LDAP connection failed", e);
}
Best Practices
1. Use Service Account for Bind
Create a dedicated LDAP service account with minimal required permissions:
- Read access to user entries
- Read access to group entries (if using group mapping)
- Password change permission (if using WRITABLE mode)
2. Enable Connection Pooling
Connection pooling improves performance:
Connection Pooling: true
Note: Connection pooling is automatically disabled when using StartTLS.
3. Use Pagination
Enable pagination to handle large directories:
Pagination: true Batch Size For Sync: 1000
4. Configure Appropriate Timeouts
Connection Timeout: 5000 Read Timeout: 30000
5. Use LDAPS or StartTLS
Always encrypt LDAP traffic in production:
# Option 1: LDAPS Connection URL: ldaps://ldap.example.com:636 # Option 2: StartTLS Connection URL: ldap://ldap.example.com:389 Start TLS: true
6. Optimize Search Filters
Use custom user search filters to limit results:
Custom User LDAP Filter: (&(objectClass=user)(!(objectClass=computer))(enabled=TRUE))
7. Regular Sync Schedule
Configure periodic synchronization for changed users:
Periodic Full Sync: false Full Sync Period: -1 Periodic Changed Users Sync: true Changed Users Sync Period: 86400
Source Code References
| Component | File Path |
|---|---|
| Provider Factory | LDAPStorageProviderFactory.java |
| Storage Provider | LDAPStorageProvider.java |
| Configuration | LDAPConfig.java |
| Context Manager | LDAPContextManager.java |
| Identity Store | LDAPIdentityStore.java |
| Operation Manager | LDAPOperationManager.java |
| User Attribute Mapper | UserAttributeLDAPStorageMapper.java |
| Group Mapper | GroupLDAPStorageMapper.java |
| Role Mapper | RoleLDAPStorageMapper.java |
| MSAD Mapper | MSADUserAccountControlStorageMapper.java |
| Read-Only Delegate | ReadonlyLDAPUserModelDelegate.java |
| LDAP Query | LDAPQuery.java |
| LDAP Object | LDAPObject.java |